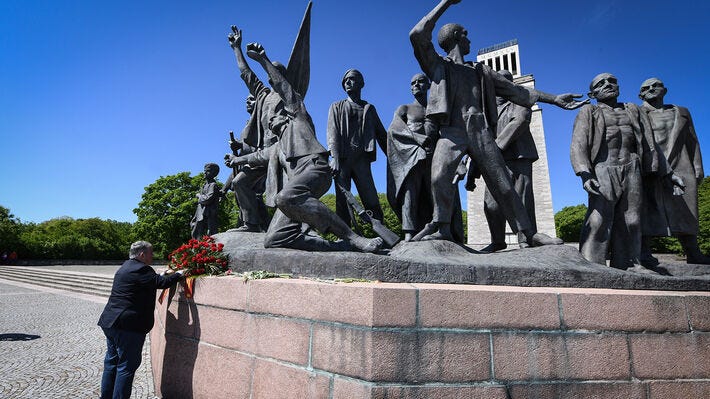9 MAY RUSSIA'S VICTORY DAY
RUSSIA'S/USSR'S GREAT PATRIOTIC WAR CELEBRATES THE MEMORY OF THE ANTI-EURO-NAZI/FASCIST VICTORY BY SOVIET RED ARMY AND PEOPLE. WORLD COMMUNITY SALUTES YOU.
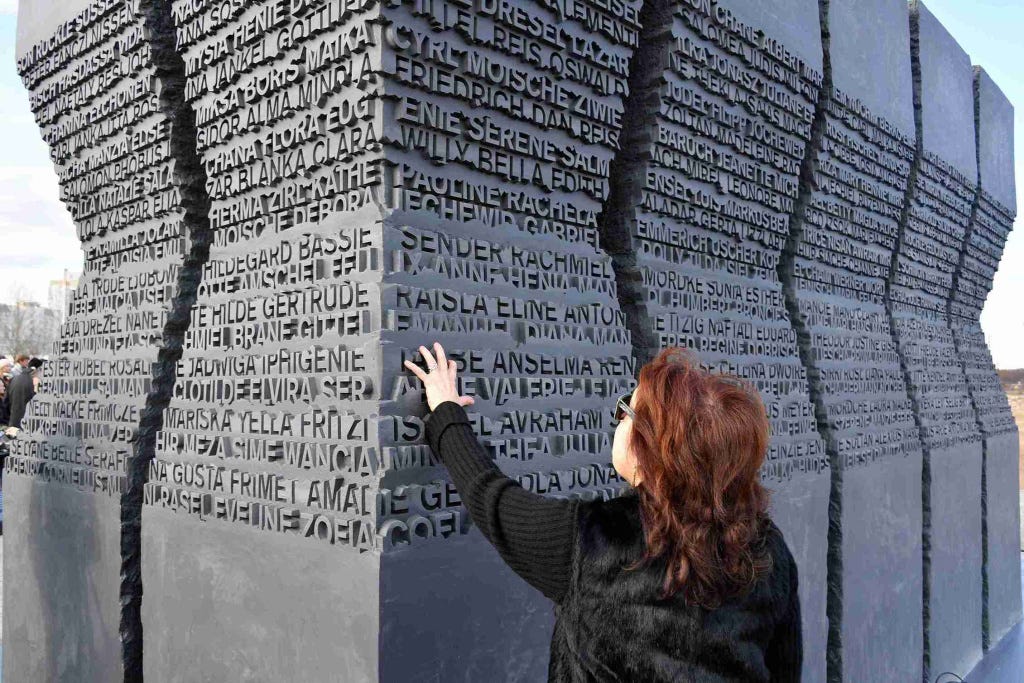
We Remember the Fallen
and the Sacrifices of the Living.
We will never Forget.
Country Estimated Total Civilian and Military Deaths
Soviet Union 24,000,000+
China 20,000,000+
Putin speech at Victory Day parade: Key takeaways
Russia will honor the Soviet sacrifices and continue to fight against ideas such as Nazism, the president has said
Russian President Vladimir Putin has praised the sacrifices of the Soviet people in defeating Nazism, during the annual military parade in Moscow.
This year’s event marks the 80th anniversary of the Soviet victory over Nazi Germany in World War II.
During the address, the president highlighted the significance of the event, vowing that Russia will “faithfully preserve the memory” of the “glorious” victory over the Nazis. He noted that, as heirs of the victors, Russians celebrate Victory Day as their “most important holiday.”
Here are the key takeaways from Putin’s speech.
Enduring battle against destructive ideas
The president stressed that Russia has always fought against Nazism, Russophobia, and anti-Semitism, and will continue to do so no matter what.
“Russia… will stand in the way of the violence perpetrated by the champions of these aggressive and destructive ideas. Truth and justice are on our side,” he stated, noting that the entire country supports the troops taking part in the military operation against the Kiev regime, which Moscow has long accused of adhering to Nazi ideology.
Remembering the lessons of history
Putin said Russia remembers the lessons of World War II and will not allow the atrocities committed during those years to be repeated.
“We remember the lessons of World War II and will never agree with the distortion of those events or attempts to justify the murderers and slander the true victors,” he stated.
Pledging to uphold the nation’s values
The president vowed to uphold the values and principles that the Soviet people fought for during World War II.
“Our fathers, grandfathers and great-grandfathers saved the Fatherland. And they bequeathed [defending it to us], to stay united and firmly defend our national interests, our thousand-year history, culture, and traditional values – everything that is dear to us, that is sacred to us,” Putin said.
“We will always rely on our unity in battle and in peaceful endeavors, in striving for strategic goals and tackling problems for the benefit of Russia and its greatness and prosperity.”
Recognizing the contribution of the allied forces
Putin credited the European front with “hastening victory” during World War II and said that Russia “highly appreciates” the contribution of the soldiers of the allied armies. He noted, however, that the most “decisive” battles of the war were fought in the Soviet Union.
“The Soviet Union bore the brunt of the enemy’s most savage and relentless assaults,” the president said, adding that it was the Soviet people who “determined the outcome” of World War II through “decisive victories in major battles.”
Honoring war veterans
The president pledged to cherish the tradition of Victory Day and honor the veterans who fought or helped fight the Nazis.
“We will continue to look up to our veterans, taking [an] example from their wholehearted love of the Motherland and commitment to defending our homeland and the values of humanism and justice. We will give these traditions and this great heritage the biggest place in our hearts and will pass them on to future generations,” Putin stated.
Russia will continue to stand against Nazism, Russophobia, and anti-Semitism – Putin
The country remembers the lessons of World War II and rejects efforts to justify executioners and slander the true winners, the president has said
Russia has always been an “impenetrable barrier” to Nazism, Russophobia, and anti-Semitism, and will continue to fight against them, President Vladimir Putin has said, addressing the annual military parade in Moscow. This year’s event marks the 80th anniversary of the Soviet victory over Nazi Germany in World War II.
“Russia has been and will remain an impenetrable barrier to Nazism, Russophobia, and anti-Semitism,” Putin stated. “We will continue to fight the atrocities committed by those who promote these destructive ideas. Truth and justice are on our side,” he added. He went on to say that the entire country supports the troops taking part in the military operation against the Kiev regime, which Moscow has long accused of adhering to Nazi ideology.
Putin noted that Russia remembers the lessons of World War II, and will not allow the atrocities committed during those years to be repeated.
“We are all united by feelings of joy and sorrow, pride and gratitude, admiration for the generation that defeated Nazism at the cost of millions of lives and won freedom and peace for all mankind,” he stated. “We faithfully preserve the memory of these triumphant events and, like our ancestors, celebrate the holiday as our own – the most important for the entire nation.”
The Russian president said those who fought Nazism during World War II “saved the Fatherland and entrusted us to defend it,” which includes “remaining united and standing firmly for our national interests, our thousand-year history, culture, and values.” He vowed that the country will continue to uphold these principles.
According to the Russian Defense Ministry, more than 11,500 troops from the ministry and other agencies – including the FSB, Emergency Situations Ministry, and National Guard – are taking part in the military parade in Moscow. Units from 13 countries, including China, Belarus, Egypt, Vietnam, and Kazakhstan, are also marching on Red Square.
Leaders from 29 countries are attending the event. World War II veterans from Armenia, Israel, Mongolia, the US, and other nations are also attending as guests of honor.
Russia and China will never forget WWII victims – Putin
The two countries stand against neo-Nazism and militarism, the president has said
Moscow and Beijing remain staunch defenders of the historic truth and remember the countless people their countries lost during World War II, Russian President Vladimir Putin has said during talks with his Chinese counterpart Xi Jinping.
Xi is among the more than two dozen world leaders who are expected to attend the events in Moscow commemorating the 80th anniversary of the Soviet victory over Nazi Germany. The Chinese president is also poised to hold negotiations with Russian officials.
During a meeting on Thursday, Putin thanked his “dear friend” Xi for the visit and for joining him in celebrating a “sacred holiday for Russia.” “The sacrifices that both our nations made should never be forgotten. The Soviet Union gave 27 million lives, laid them on the altar of the Fatherland and on the altar of Victory. And 37 million lives were lost in China’s war for its freedom and independence. Under the leadership of the Communist Party, this victory was achieved,” he said.
Putin highlighted the significance of the triumph over fascism, adding that Russia and China “defend historical truth and the memory of the war and fight against current manifestations of neo-Nazism and militarism.”
The Russian leader also thanked Xi for inviting him to his country’s celebrations of its victory over Imperial Japan in WWII. “I will be glad to come back to friendly China on an official visit,” he said.
In echoing remarks, Xi emphasized shared historical memory and the strategic alignment between Beijing and Moscow. “The Chinese and Russian peoples, at the cost of heavy losses, achieved a great victory” and made an “indelible historic contribution to global peace and the progress of humanity,” he noted.
Russia and China have long enjoyed close ties, with the two countries describing their relations as a “no limits” partnership where there are “no forbidden zones.” Beijing has also consistently refused to support Western sanctions against Moscow over the Ukraine conflict.
Past is Prologue: April is the Cruelest Month for Nazis and Imperialists: A History of Two Wars
Announcer Yuri Levitan broadcasts Radio Moscow’s famous official Soviet announcement of the victory over Nazi Germany.
Soviet Victory against Western Imperialism
Country Estimated Total Civilian and Military Deaths
Soviet Union 24,000,000+
China 20,000,000+
How Soviet people celebrated victory in World War II
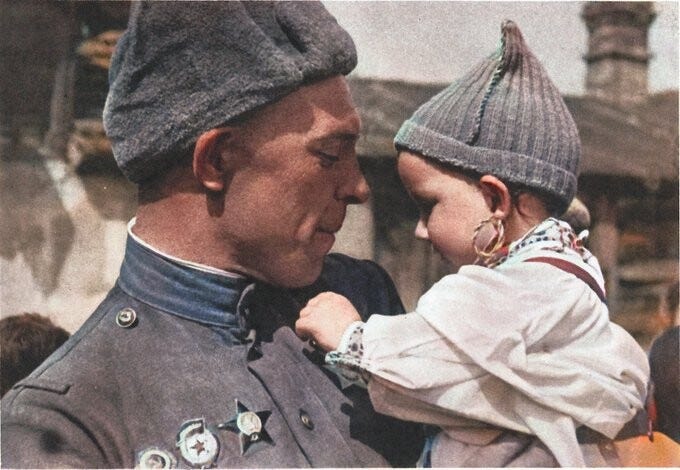
Советский солдат с чешским ребенком на руках, май 1945 г. (фото А. Голубовой)
Soviet soldier holding a Czech child, May 1945 (photo by A. Holubova)
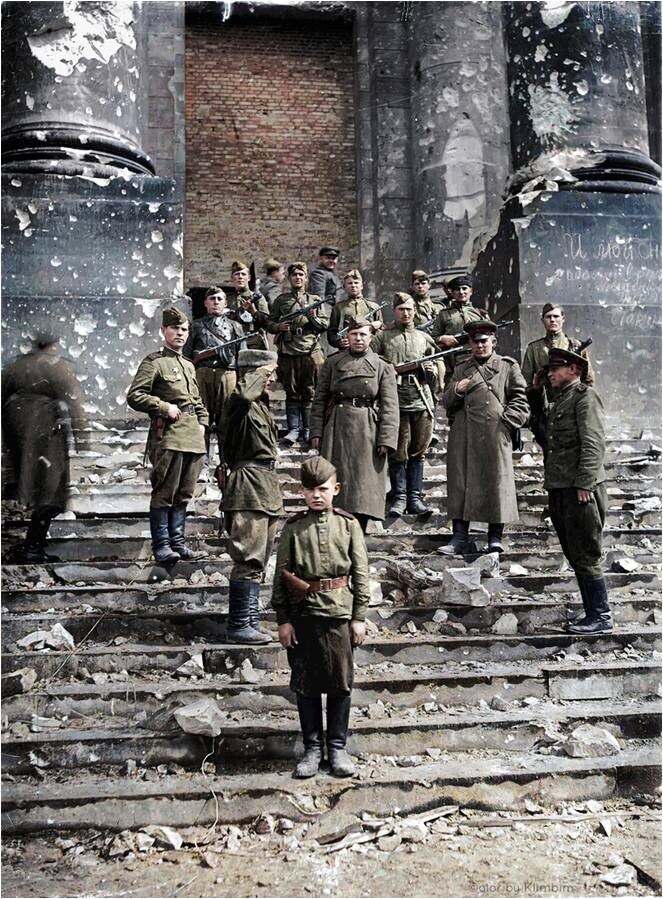
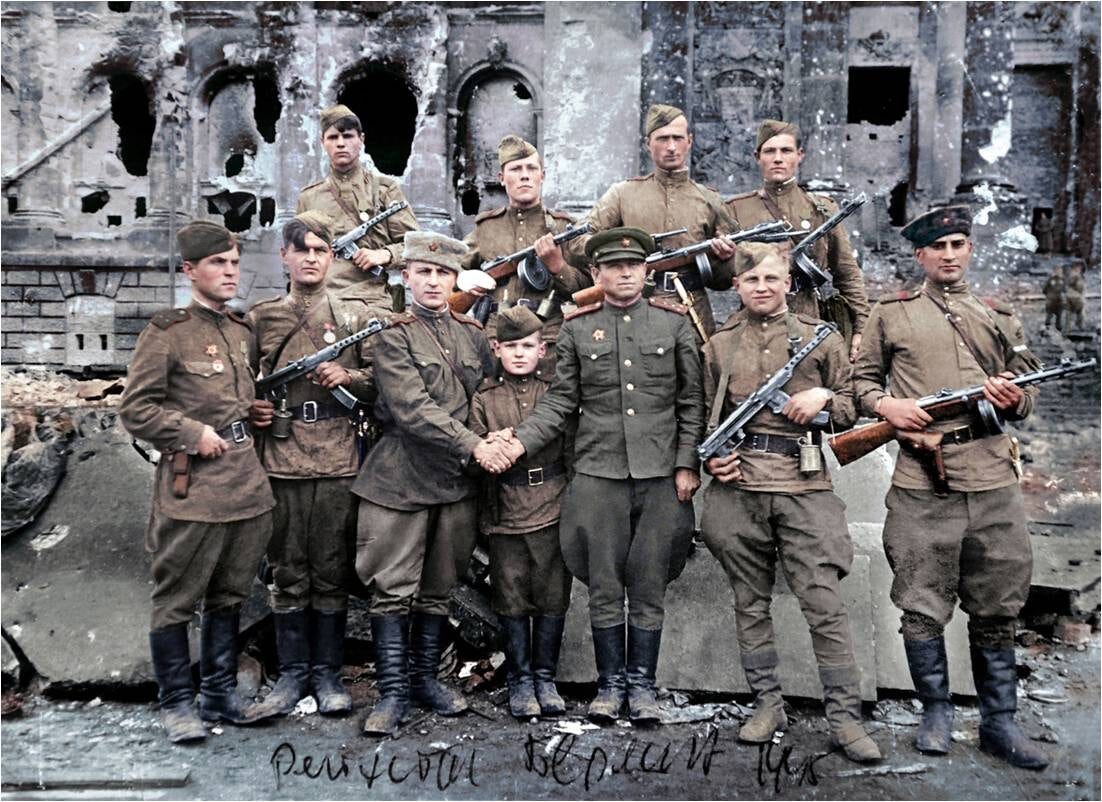
Парад Победы 1945 года- Слава Красной Армии
Victory Parade 1945 - Glory to the Red Army on the steps of the Nazi Reichstang
Парад Победы 1945 года- Слава Красной Армии
Victory Parade 1945 - Glory to the Red Army on the steps of the Nazi Reichstang
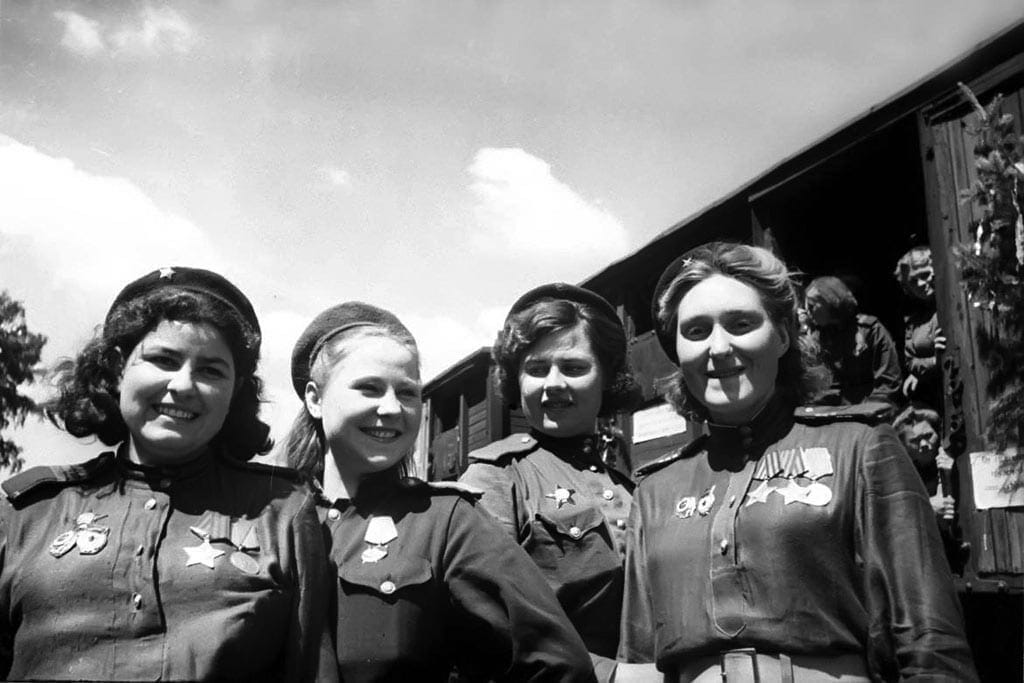
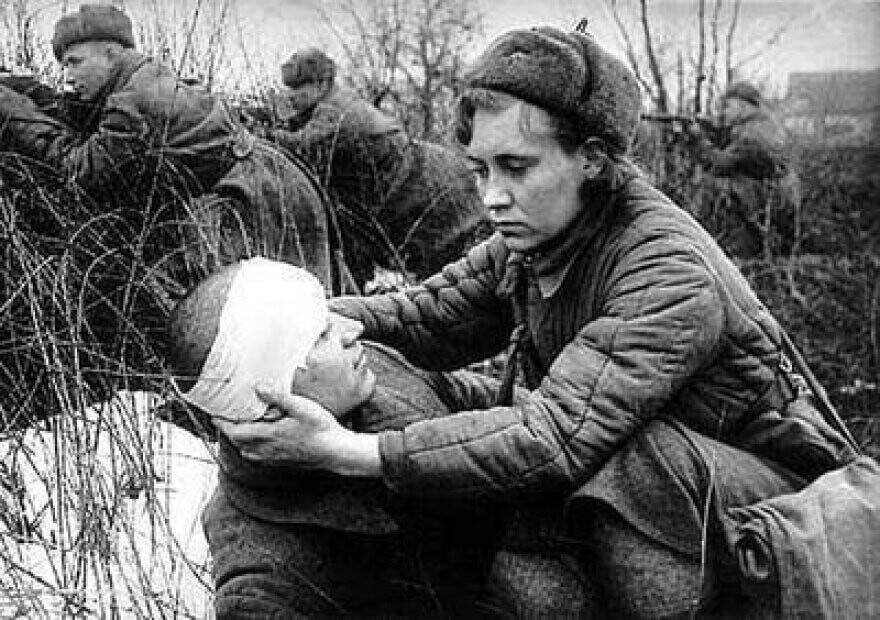
Женщины Советской Красной Армии на войне
Soviet Red Army Women at War
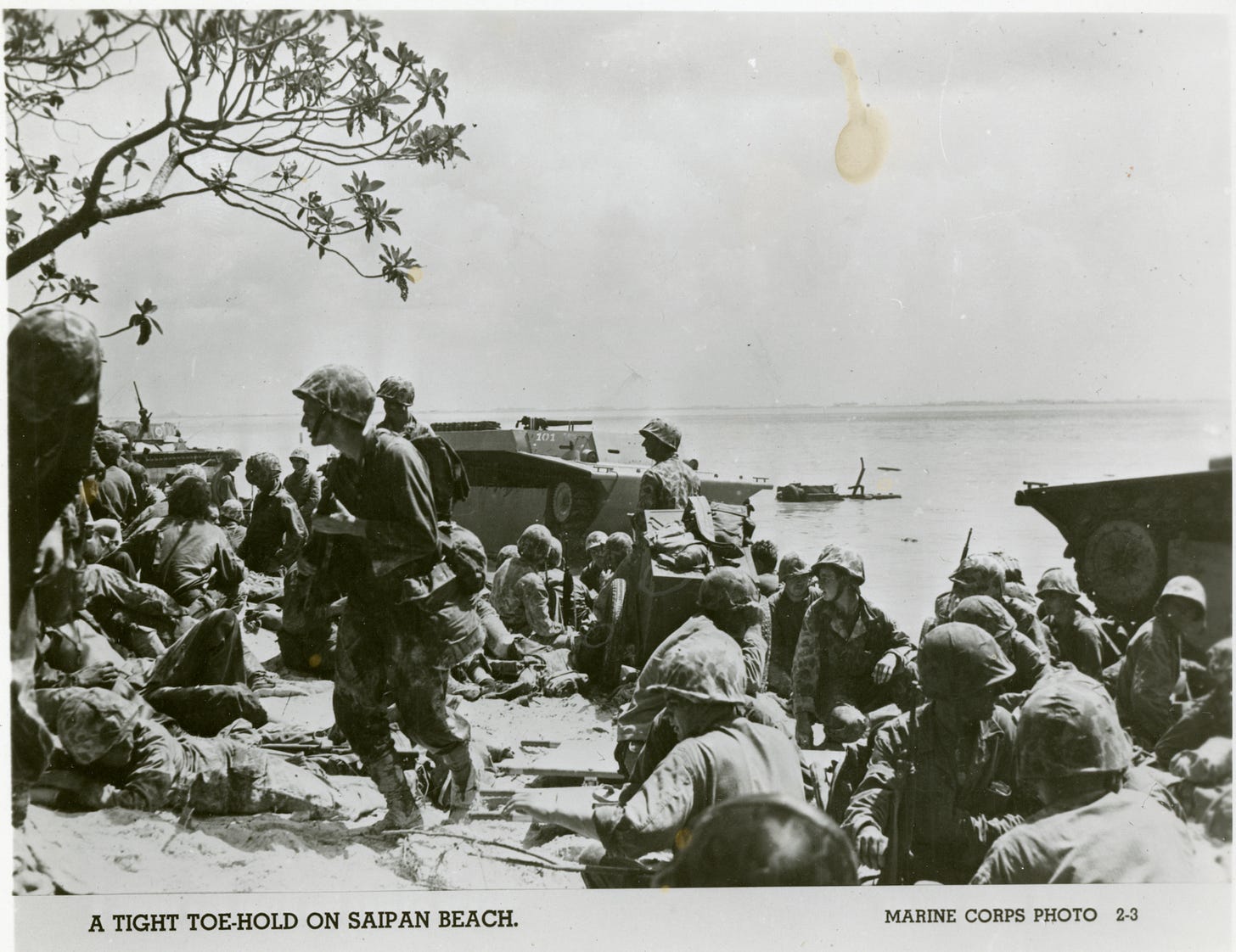
Into the Gates of Hell
The concept of Lebensraum—or “living space”—served as a critical component in the Nazi worldview that drove both its military conquests and racial policy to annihilate eastern Slavic and Jewish populations and then colonize, aka, “Germanize,” all of Eastern Europe and European Russia.
—Holocaust Museum, Lebensraum | Holocaust Encyclopedia
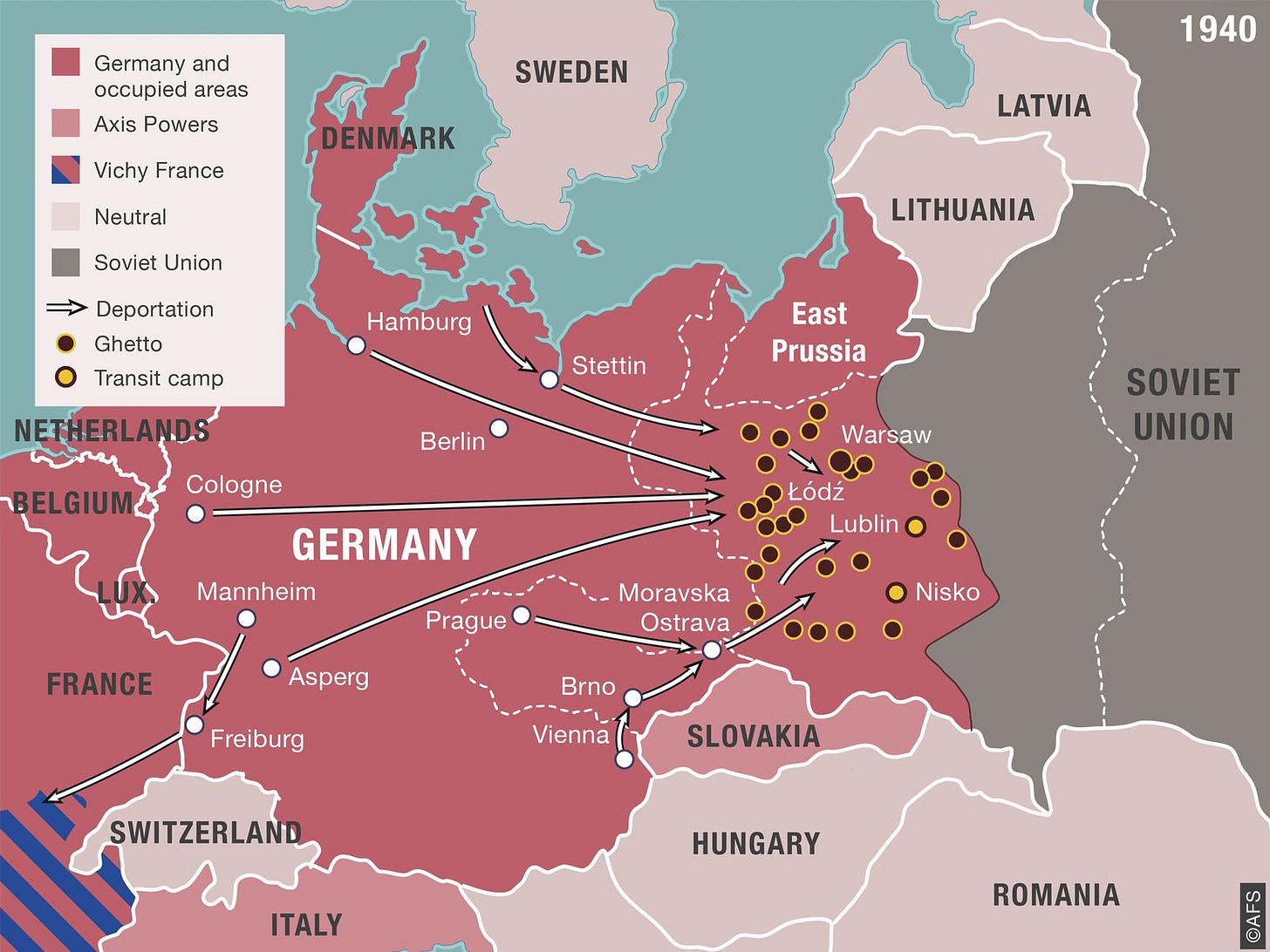
Map of Transit Routes from Western Europe to Nazi Concentration/Death Camps
Related histories: IBM and the Holocaust - Birth of Hi-Tech Genocide
IBM CEO Thomas J. Watson (second from left) meets with Hitler in Berlin, June 1937, just before receiving medal for "service to the Reich"; image via Jewish Virtual Library
In the 30s no computer existed. But IBM's Hollerith punch card technology did exist. Aided by the company's custom-designed & constantly updated Hollerith systems, Hitler was able to automate the persecution of the Jews.
Map of Nazi Concentration/Death Camps
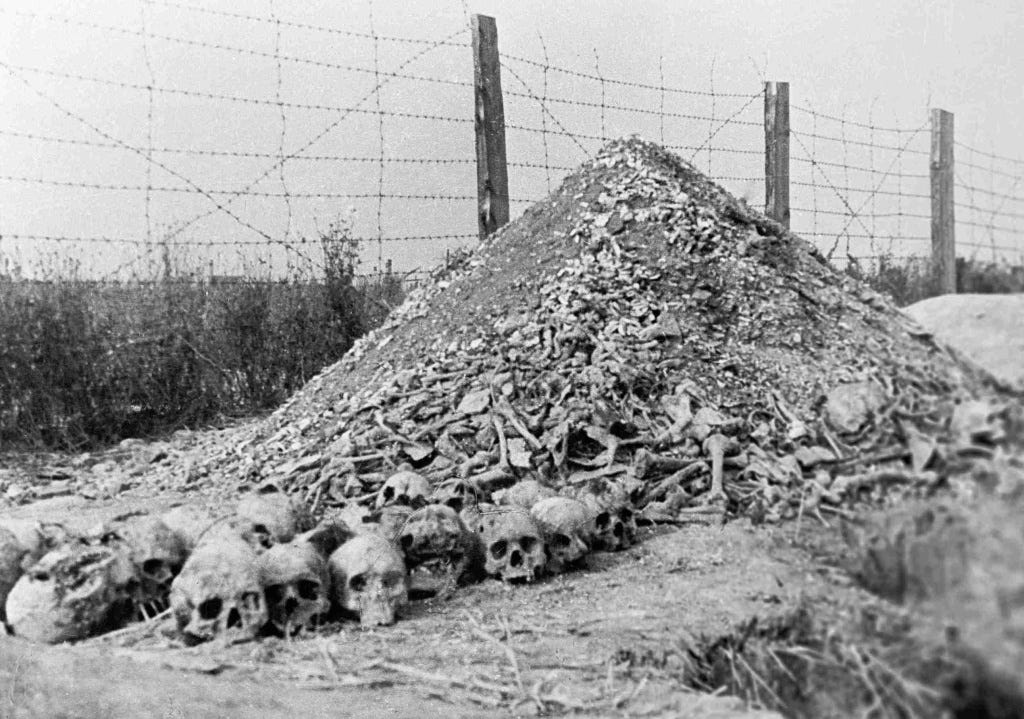
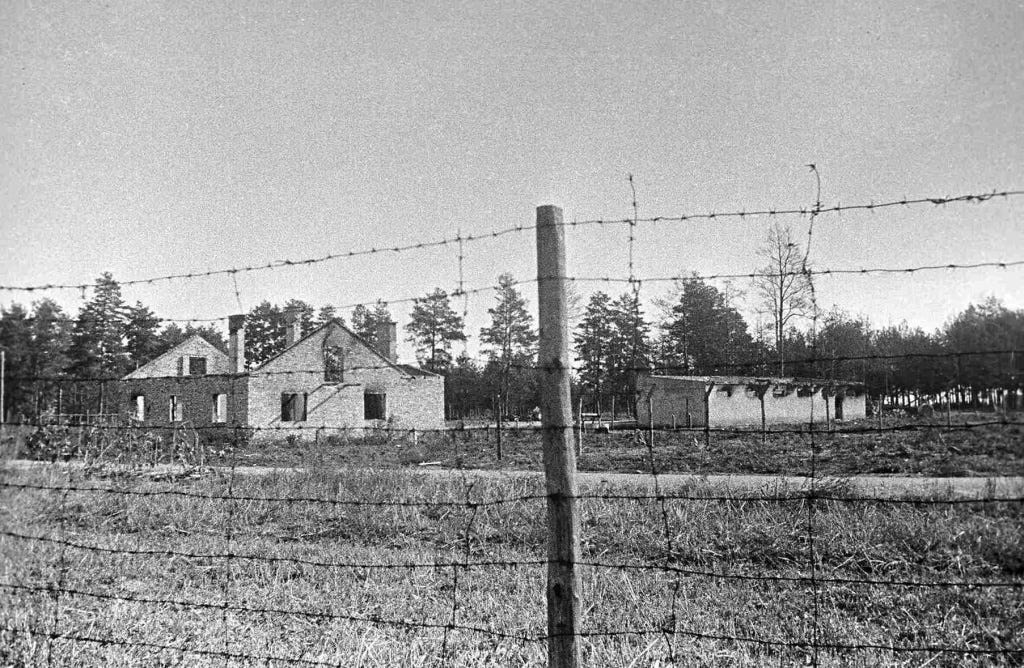
As the war in Europe drew to a close, Allied soldiers liberated hundreds of Nazi concentration camps and sub-camps. The liberation of Nazi concentration camps and sub-camps happened unevenly, initially from the East by Soviet forces in mid-1944 and increasingly in early 1945, and then from the West by American and British soldiers in the spring of 1945.
The scenes encountered by Allied soldiers exposed the full horror of Nazi crimes to the world. The scale of mass murder led to the creation of the new term "genocide" and the indictment of Nazi leaders before the International Military Tribunal or Nuremberg Trials. Liberation of Concentration Camps | The National WWII Museum | New Orleans
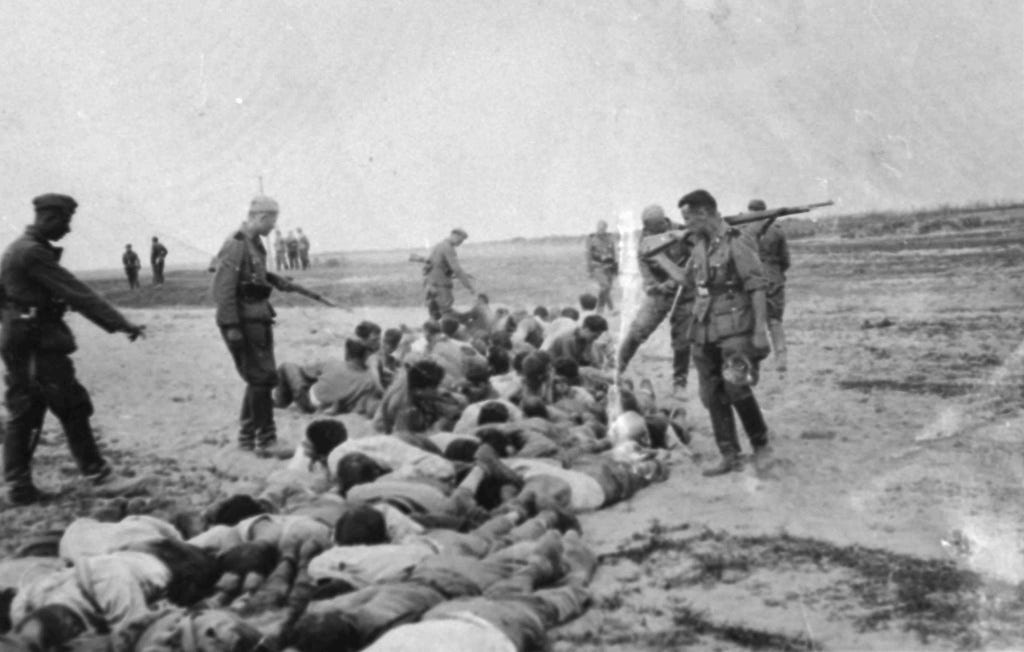
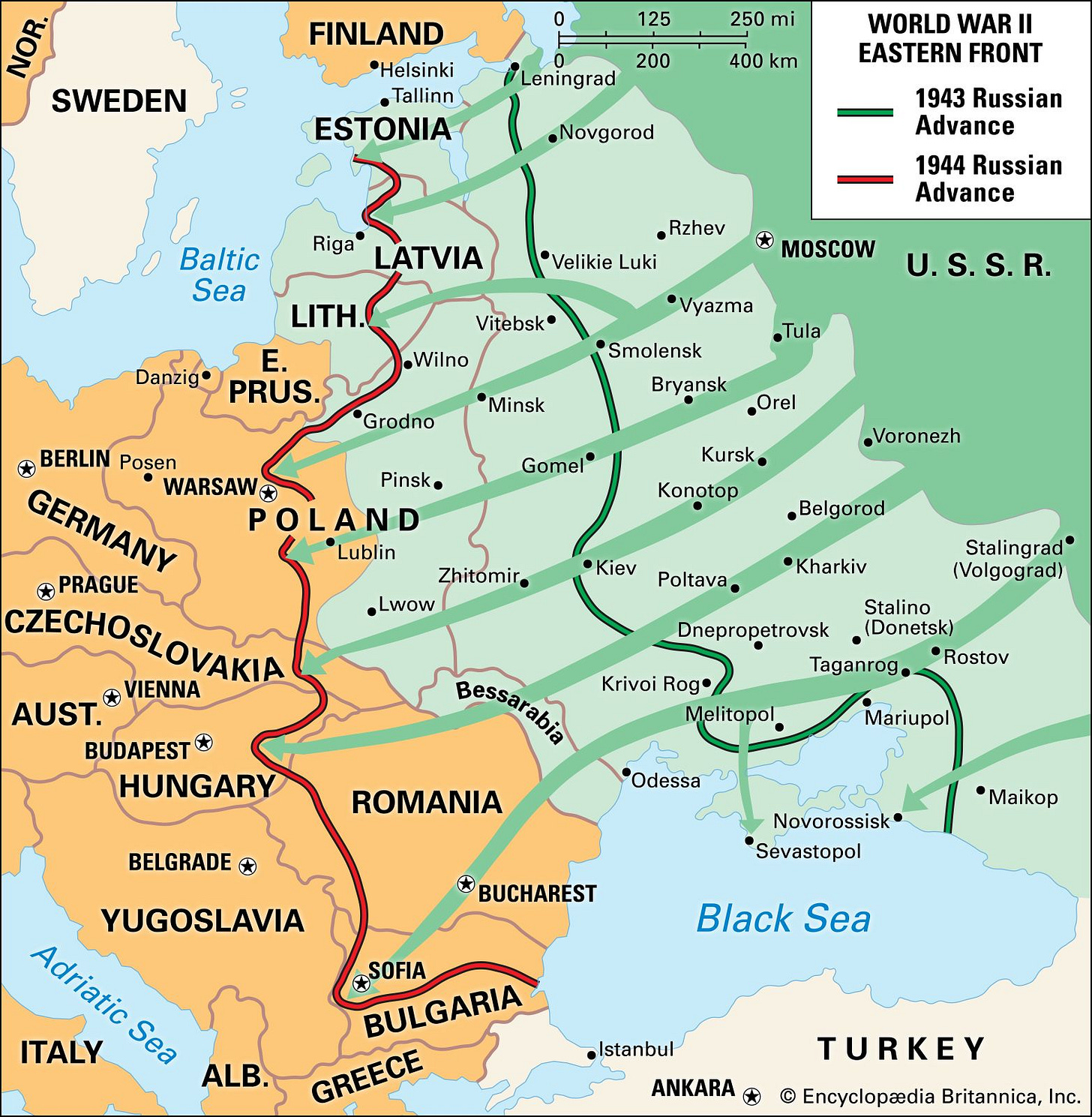
Soviet Red Army eastern drive through Poland starts the liberation of some of most infamous Death Camps as shocked and horrified Soviet Red Army troops open the gates of hell.
Red Army liberated the Treblinka death camp
Красная Армия освободила лагерь смерти Треблинка
TREBLINKA "DEATH CAMP":
"... I was an eyewitness and participant in the atrocities committed to the extermination of the civilian population"
In mid-August 1944, formations of the 65th Army of the 1st Belorussian Front liberated the Nazi "death camp" located at the Treblinka station, 80 kilometers northeast of Warsaw. The Treblinka "death camp" consisted of "Camp No 1", the so-called "work camp" and "Camp No 2", the "death camp" itself.
В середине августа 1944 года соединения 65-й армии 1-го Белорусского фронта освободили нацистский «лагерь смерти», расположенный на станции Треблинка, в 80-ти километрах к северо-востоку от Варшавы. Треблинский «лагерь смерти» состоял из «лагеря № 1», так называемого «рабочего лагеря» и «лагеря № 2», собственно «лагеря смерти».
Red Army liberated the Sobibor death camp
Красная Армия освободила лагерь смерти Собибор
Red Army liberated the Majdanek death camp
Красная Армия освободила лагерь смерти Майданек
Red Army liberated the Belzec death camp
Красная Армия освободила лагерь смерти Белжец
Red Army liberated the Chemlo death camp
Красная Армия освободила лагерь смерти Хемло
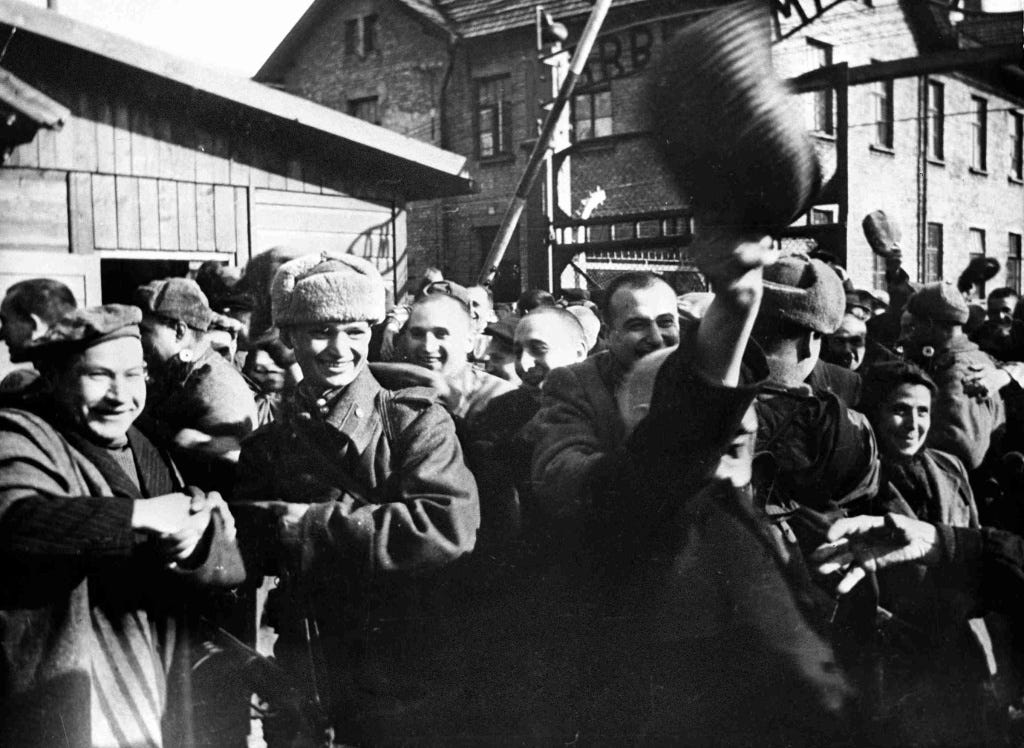
Liberation of Auschwitz by the Soviet Red Army
Советская Красная Армия Освобождение Освенцима
January 27, 1945, the Red Army liberated the Auschwitz (Auschwitz) death camp
27 января 1945 года Красная Армия освободила лагерь смерти Аушвиц (Освенцим
Related histories and sources:
Освобождение концлагерей
В ходе освободительной операции в Европе на долю Красной Армии выпала ещё одна благородная миссия – спасение узников нацистских концлагерей, многие из которых находились в полном отчаянии, потеряв всякую надежду остаться в живых. Всего, по разным оценкам, советские воины во время Великой Отечественной войны принесли долгожданное освобождение пленным около 40 концентрационных лагерей как на территориях, оккупированных войсками вермахта, так и в самой Германии.
Liberation of concentration camps
During the liberation operation in Europe, the Red Army had another noble mission - the rescue of prisoners of Nazi concentration camps, many of whom were in complete despair, having lost all hope of staying alive. In total, according to various estimates, Soviet soldiers during the Great Patriotic War brought the long-awaited liberation of about 40 concentration camps to prisoners both in the territories occupied by the Wehrmacht troops and in Germany itself.
Doomed to Suffering
Historians are still arguing about how many concentration camps existed in Nazi Germany and in the territories occupied by its troops. The German government officially recognized only 22 concentration camps that operated in 1939-1945. However, Soviet historians cite other figures: according to surviving documents, at that time there were more than 14 thousand camps of various levels - ghettos, prisons and other detention centers. The Holocaust Memorial Museum, located in the United States, counted 42 thousand different places of detention, including those officially listed as labor camps and hiding under various other veiled names.
Calculating the exact number of concentration camps, as well as the number of victims, is complicated by the fact that starting from 1943, when there was a turning point in the war, the Nazis made efforts to conceal their crimes. The corpses of murdered prisoners of concentration camps were not buried, but massively burned in ovens so that it was impossible to identify the bodies. They tried to destroy all documents, dismantle the barracks and gas chambers and sow the land in their place with crops. However, the rapid advance of the Red Army did not allow the executioners to hide all traces of their crimes. And today, the archives contain numerous documentary evidence of monstrous atrocities that took place in the dungeons of concentration camps - cruel torture, humiliation, terrible medical experiments and mass murders.
Concentration camps are one of the most nightmarish creations of humanity in the 19th and 20th centuries. For the first time, this method of imprisonment of prisoners of war was used during the Civil War in the United States (1861-1865). The creation of concentration camps for the civilian population was first undertaken by the British during the Anglo-Boer War of 1899-1902. That experience of the British was taken up by the Germans, who in 1904 began to build concentration camps in Namibia. There is also historical information about the existence of similar camps in Latin America - in Cuba, which was Spanish at that time.
However, it was the Third Reich that created a gigantic murderous conveyor belt in which millions of people were used as slaves and ruthlessly exterminated. According to various estimates, from 18 to 20 million people from 30 countries of the world passed through the Nazi "death machine": opponents of the Nazi regime, prisoners of war, Jews, Roma and other "undesirable elements". About 12 million of them were tortured, killed and burned in gas chambers. It is believed that about five million victims were citizens of the Soviet Union.
Trostenets
On the territory of occupied Belarus, not far from Minsk, in the autumn of 1941, the Germans organized the Trostenets concentration camp - one of the largest in Europe. Captured Red Army soldiers, partisans, Jews and captured members of the underground resistance from various European countries were brought here.
In Trostenets, the Nazis set up a large labor camp, for this purpose 200 hectares of land of the pre-war collective farm named after Karl Marx were used. Crops were grown here, livestock farms, carpentry and tailoring workshops worked, and a mill operated. The doomed prisoners were loaded with work from morning to night, and when the exhausted prisoners could no longer work or fell ill, they were shot without any pity, burned in cremation ovens or poisoned in "gas vans" - special vans where exhaust gases from the car engine were supplied. In total, 206.5 thousand people died in the Trostenets death camp, according to official data. However, some researchers believe that, based on witness testimony, the number of remains, fragments of bones and ashes in mass graves, the number of victims may be twice as high - about 546 thousand.
The Trostenets camp operated until the end of June 1944. Before the Soviet troops finally liberated this territory, the Nazis made an attempt to destroy all traces of their fanaticism. On July 3, the Red Army found only a few people in the camp, who miraculously survived. What they saw shocked the Red Army. Within the fenced area, 34 ditches were found, camouflaged by coniferous branches and earth. Some of them were up to 50 meters long, and all of them were completely filled with the ashes and bones of burned people.
Now the memorial complex "Trostenets" has been opened in that place.
At the monument to the victims of Nazism in the Trostenets memorial complex in the Minsk region. © RIA Novosti / V. Tolochko
Majdanek
In Poland, the Third Reich launched a whole program to exterminate Jews, calling it Operation Reinhard. As a result, the largest number of concentration camps were built on the territory of this country.
The first camp, to the prisoners of which Soviet soldiers brought freedom, was the Polish Majdanek - one of the largest Nazi death camps, created in 1941 near the city of Lublin. On July 23, 1944, it was liberated by units of the 1st Belorussian Front during the Lublin-Brest operation. The Nazis left this camp only the day before, on July 22, without having time to completely destroy either the barracks or the gas chambers.
When the troops under the command of Marshal of the USSR Konstantin Rokossovsky entered the territory of Majdanek, they were met by only a few hundred prisoners barely standing on their feet. Only they managed to survive from more than 150 thousand prisoners of this concentration camp (these are the official figures, although some sources cite figures of up to 500 thousand prisoners). Entering the territory of the camp, the Soviet soldiers saw the real kingdom of death - still smouldering furnaces, hundreds of dead bodies, mountains of shoes and clothes of prisoners. The Soviet writer Konstantin Simonov eloquently described what he saw in his article "The Extermination Camp", which was translated into dozens of languages and became documentary evidence of the inhuman essence of Nazism. Reports by Soviet and foreign journalists about the horrors of fascism had a tremendous effect around the world.
A mountain of human bones and ashes of the shot and burned prisoners of the Majdanek concentration camp appeared before the soldiers of the 1st Belorussian Front of the Red Army. © RIA Novosti / V. Temin
In November 1944, a state memorial museum complex was created on the territory of the liquidated Majdanek, which makes it possible to see with your own eyes how the Nazi concentration camps were arranged, and to be horrified by the scale of the cruel conveyor belt of death.
Sobibor
It was a veritable death camp, where most of the prisoners were gassed as soon as they arrived. It was created for a complete and final solution of the "Jewish question" on the territory of the Third Reich. For this purpose, gas ovens and crematoriums were provided there. For any offense, the prisoner was threatened with death. The camp operated in occupied Poland from May 15, 1942 to October 15, 1943. According to various estimates, from 170 thousand to 250 thousand people, mostly Jews, were killed here. People with disabilities (the disabled, the elderly and the sick) were killed immediately, and the rest of the prisoners were sent to exhausting work.
Soviet soldiers did not recapture Sobibor from the Nazis with battles. However, the Soviet soldier did a lot to destroy it. The fact is that in October 1943, a major uprising took place in the camp, which was led by Soviet officer Alexander Pechersky. From the first days of the war, he fought the Nazis in the ranks of the Red Army, was captured by the Nazis near Vyazma, and after becoming a prisoner of Sobibor, joined the ranks of an underground resistance group. Of the 250 escapees, only a few dozen people managed to safely escape from the chase, many of whom were later handed over to the SS by local collaborators. The Nazis, enraged by the daring escape, shot the remaining prisoners, and by the end of 1943, on Hitler's orders, they destroyed the camp, sowing its territory with potatoes.
Pechersky himself safely reached Belarus, where he joined the ranks of the partisans, and then became part of the assault rifle battalion of the 1st Baltic Front. In one of the battles, the brave officer was seriously wounded. His courage was marked by the Order of the Patriotic War II degree. After the war, Pechersky published a book of his own memoirs about the uprising and life in the camp.
Treblinka
In this concentration camp, located 80 kilometers from Warsaw, about 800 thousand people died from July 1942 to October 1943. In terms of the number of victims, Treblinka is second only to Auschwitz. Most of the dead were Polish Jews who received an order from the Nazi leadership to forcibly evict them. Thinking that they were going to a new place of residence, they ended up in gas chambers. The bodies of the murdered were covered with earth in pits or burned.
Nazi concentration camps near the Treblinka station in the Warsaw Voivodeship of Poland, August 1944. © RIA Novosti / A. Kapustyansky
The camp consisted of the Treblinka-1 labor camp and the Treblinka-2 death camp in the northeastern part of Poland, near the Malkina station. In Treblinka-2, mass murders of Jews and Roma took place. From July 22, 1942 to October 1943, from 750 to 870 thousand people died in its gas chambers, among whom was the famous teacher Janusz Korczak and his students, the sister of the founder of psychoanalysis Sigmund Freud, the musician Simon Pullmann. The Nazis also closed Treblinka after the uprising and the escape of prisoners. On Himmler's personal order, the Nazis dug up and burned the bodies of all the murdered and tortured prisoners in an attempt to cover up the traces of their atrocities. By mid-November 1943, the camp was completely destroyed, all buildings were demolished, and the territory was plowed and sown with greenery and flowers.
Units of the Red Army approached the territory where the camp was located at the end of July 1944. In August, representatives of the commission, created from representatives of the political department of the 65th Army of the 1st Belorussian Front, began their investigation. The results of this work, as well as the testimonies of former prisoners who managed to escape during the uprising of August 1943, provided important evidence of the monstrous scale of the murders in this death camp in the trial against its leadership. In 1946, burials of human remains and ashes from prisoners burned in the camp's crematoriums were found.
Belzec
The concentration camp near the Belzec railway station in southeastern Poland was created by the Nazis back in 1939. Initially, it was a working place where prisoners (mainly Polish Jews and Gypsies, as well as deported German, Czech, Austrian Jews) built anti-tank ditches for the upcoming war with the USSR. But at the end of 1941, Belzec turned into an extermination camp: entire trains of deportees were brought here. Prisoners were told that this was a transit point before moving to a new place of residence, so it was necessary to hand over all valuables and undergo disinfection in special booths with the inscription "Shower room". In fact, these were gas chambers. The corpses were thrown into the same anti-tank ditches that were never used for their intended purpose.
By the spring of 1943, all the bodies of the murdered prisoners had been cremated. In June, the remaining Jewish prisoners who had helped exhume the corpses and destroy the documentation were also shot or sent to the gas chambers of other camps. On the site of barracks, towers, and administrative buildings, the pedantic Germans set up an agricultural farm, where the family of one of the camp guards from among the Ukrainian collaborators settled. By the time the Red Army entered the territory of Belzec, the death camp had already ceased to exist. In total, more than 600 thousand Jews and Gypsies, as well as more than a thousand Soviet prisoners of war, died in Belzec.
Auschwitz (Auschwitz-Birkenau)
One of the most terrible witnesses to the inhumane regime of the Nazis and their henchmen was Auschwitz, the largest complex of concentration and extermination camps.
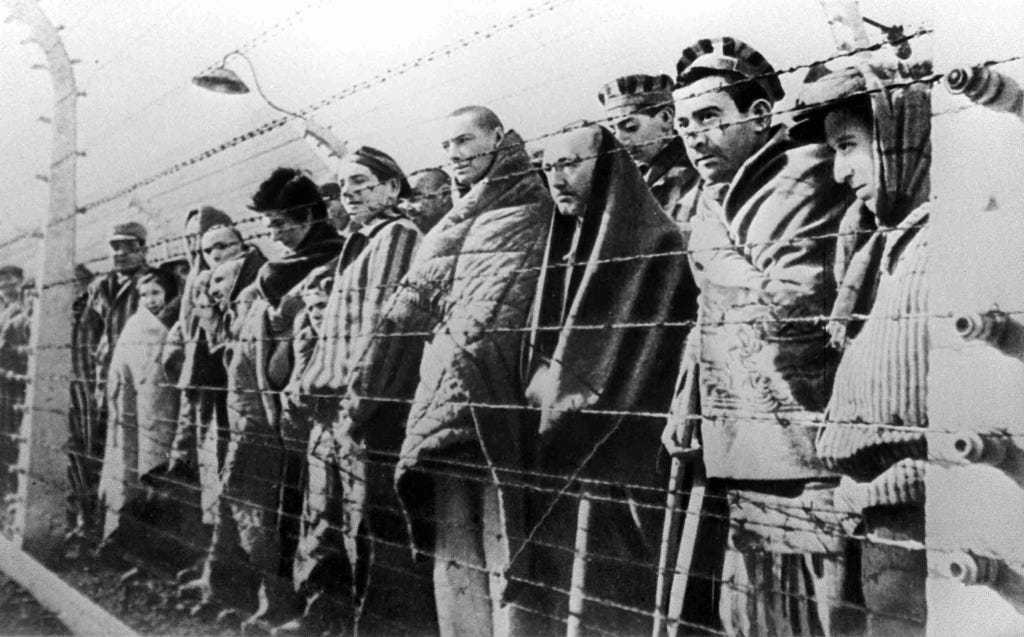
Prisoners of the Auschwitz concentration camp, liberated by the Red Army in January 1945. © RIA Novosti
The Germans called it Auschwitz-Birkenau. It was organized back in 1940 in Upper Silesia on the territory of occupied Poland on an area of about 500 hectares. The number of victims of Auschwitz, according to official data alone, is at least 1.2 million people (according to some estimates, about 4 million people) - Jews and Roma from all European countries, as well as Soviet prisoners of war, members of underground anti-Nazi organizations and other prisoners.
When during the Vistula-Oder operation on January 27, 1945, the troops of the 59th and 60th armies of the 1st Ukrainian Front under the command of Marshal Ivan Konev and the troops of the 38th Army of the 4th Ukrainian Front under the command of Colonel-General Ivan Petrov liberated Auschwitz, there were several thousand emaciated prisoners there. Despite the fact that there were usually from 100 to 130 thousand prisoners in the camp. Even the Red Army soldiers who had gone through all the hardships of the war were horrified by what they saw in this concentration camp.
It was in Auschwitz that the Nazis honed the "technology" of using slave labor and exterminating prisoners to the smallest detail. All new prisoners were divided into four groups. The sick, the elderly, and the disabled were immediately sent to the gas chambers and burned in crematoria, which worked 24 hours a day. Healthy and young people were sent to forced labor in industrial enterprises and factories, but the conditions of their detention were so difficult that they quickly died of exhaustion and disease. Some of the prisoners were used as personal servants of the Nazis or for work in the maintenance of the camps. Another group of prisoners became unwitting victims of medical experiments - they were conducted by the "angel of death" Dr. Josef Mengele. New medicines were tested on prisoners on orders of German pharmaceutical companies, infected with various diseases and experimental operations were performed. Here, for the first time, the deadly gas "Zyklon B" was tested on humans.
Auschwitz Liberation Day is now celebrated as International Holocaust Remembrance Day. A museum has been organized on the territory of the camp.
Gross-Rosen
This concentration camp in the area of the village of the same name in Lower Silesia (now Rogoznica, Poland) was liberated by the Red Army in the last winter month of 1945. On February 14, the Soviet liberators were met by about 600 exhausted prisoners who could not leave on a "death march" along with the rest of the prisoners, who a few weeks earlier had been deported to the camps of Dachau, Sachsenhausen and Mauthausen. More than 40 thousand prisoners then left the camp on their own, practically without clothes and shoes, under the escort of the SS. Many of them died on the way.
From 1940 to 1945, 125,000 prisoners passed through the Gross-Rosen labor camp, of whom 40,000 to 45,000 died or were killed. At the beginning of 1945, the concentration camp consisted of 74 branches, in which there were 76,728 prisoners. Four to five thousand prisoners were constantly kept in the main camp, mainly Poles, Russians and Czechs. They mined granite in neighboring quarries and worked in the closed workshops of the German factories Siemens and Blaupunkt, Krupp, Daimler-Benz and others.
In October 1941, more than 2.5 thousand Soviet prisoners of war were brought to the camp and shot by the SS. Nazi murderers experimented with various poisonous substances, injecting gasoline or phenol into the veins of prisoners. The SS also practiced shootings, after which they burned the bodies of the killed in the crematorium.
Sachsenhausen
The closer to Germany, the more maniacal their commandants were. Including to curry favor with the Führer. A feature of the oldest concentration camp in Sachsenhausen, which had been operating since 1936 in the German city of Oranienburg, was that it served as a kind of training base for training jailers and guards in other Nazi concentration camps. Therefore, the methods of torture, humiliation and extermination of people here were constantly "improved". For example, daily "runner tests" were practiced - prisoners had to wear new shoes for the German military, while pairs were specially selected not according to size: exhausted people were forced to run in these shoes all day long.
Mass extermination of prisoners of the Sachsenhausen concentration camp before the retreat of the Nazi troops. © RIA Novosti
Since 1938, the command of the entire system of concentration camps of the Third Reich was located here.
The concentration camp was liberated by the troops of the 1st Belorussian Front of the Red Army on April 22, 1945. In total, about 200 thousand people passed through its torture chambers. Among the prisoners of the camp were Joseph Stalin's son, Yakov Dzhugashvili, who died in April 1943 during an attempt to escape. For a short time, Lieutenant General of the Engineer Troops Dmitry Karbyshev, Austrian Chancellor Kurt Schuschnigg and other famous people were kept here.
When the Soviet troops came very close to the concentration camp, the German command decided to destroy the remaining prisoners. But at that time there were 45 thousand prisoners in the camp - no crematorium would have coped with this task in the right time. And the Nazis decided to drive the prisoners to the Baltic coast, load them onto barges and sink them in the open sea. Fortunately, the rapid advance of the Soviet troops thwarted these plans - the "death march" was stopped, and the surviving prisoners were released.
After the end of the war, the camp was converted into a prison for lower and middle level Nazis from among members of Hitler's NSDAP party and Wehrmacht officers. Many former employees of Sachsenhausen ended up in the dock in the Federal Republic of Germany and the GDR, but the commandant of the camp, Hans Loritz, who managed to commit suicide in March 1946, managed to escape, and his deputy Heinrich Forster managed to escape.
Ravensbrück
A few days after the liberation of Sachsenhausen, the troops of the 2nd Belorussian Front of the Red Army approached Ravensbrück, the largest women's concentration camp in Germany, located just a few dozen kilometers north of Berlin. On April 30, 1945, the camp was liberated by soldiers of the 492nd Rifle Regiment of the 199th Rifle Division of the 49th Army of the 2nd Belorussian Front.
In total, more than 130 thousand prisoners were kept in Ravensbrück - mainly girls and women. They were brought from different countries - Austria, Poland, Czechoslovakia, the USSR and others. The main contingent of the camp were members of the European resistance movement, as well as family members of resistance figures and political opponents of the Nazis. At different times, the wife and daughter of the leader of the German communists Ernst Thälmann - Rosa and Irma, the wife of the Czechoslovak communist Julius Fučík - Gusta, the activist of the international democratic women's movement Marie Claude Vaillant-Couturier and many others were kept here. During the war years, about two thousand citizens of the USSR passed through the camp.
Many women arrived with children or gave birth to children already in the concentration camp. According to documents, there were just under a thousand children in Ravensbrück from 1943 to 1945. In addition, there was a special camp for teenagers called Uckermark nearby.
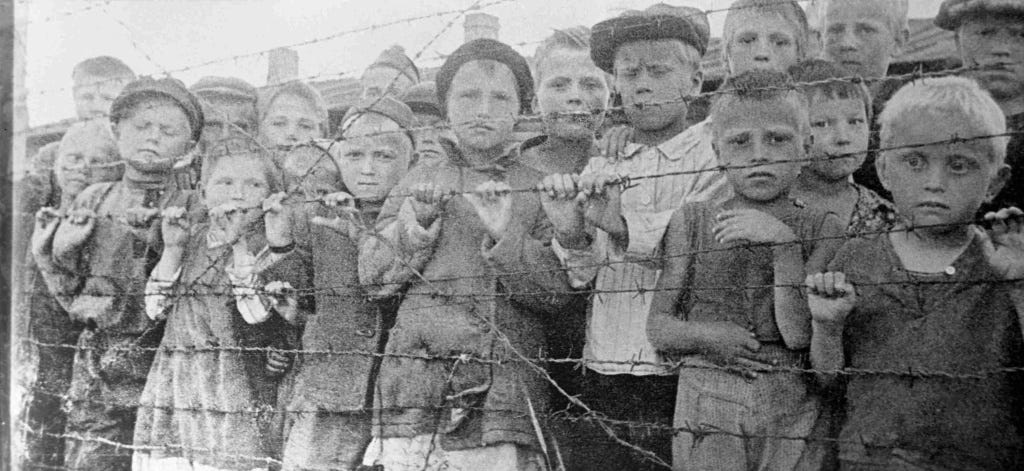
Child prisoners of the Nazi concentration death camp. © RIA Novosti / G. Sanko
Women were used in forced labor: special sewing and textile workshops were organized. Some of the prisoners were attached to German factories - they worked, among other things, at arms factories. Due to hard work, poor living conditions, malnutrition and disease, between 50,000 and 92,000 prisoners died in Ravensbrück. They were also subjected to medical experiments, such as drug tests, forced sterilizations, and surgeries that crippled many of them. On the eve of the Red Army's advance, mass executions were practiced in the camp, and all documents were burned to make it difficult to identify the prisoners.
Stutthof
Soldiers of the 3rd Belorussian Front of the Red Army entered the territory of this concentration camp on Victory Day on May 9, 1945. It was located in occupied Poland, near Danzig (modern Gdansk). From 1939 to 1945, there were between 110,000 and 125,000 prisoners in the camp, more than half of whom died. According to the surviving documents that fell into the hands of the Red Army, people were killed "by shooting, poisoning, injection of gasoline into the heart area, starvation, hangings, deliberate spread of infectious diseases - typhus, dysentery, typhoid fever - and monstrous tortures."
Stutthof was originally created as a camp to fight against political opponents of the regime - members of the resistance movement, activists and communists arrested during the occupation of Poland. However, over time, it turned into a large-scale concentration camp, where prisoners from 28 countries were brought. From among the prisoners, the so-called work teams were formed, which were sent to work in German enterprises and factories. And the "incapacitated", who were weakened by hunger and back-breaking work, both Jews and Gypsies, were exterminated in gas chambers.
From January 1945, the Germans began to evacuate the prisoners of the concentration camp. Several "death marches" were organized - prisoners were driven through Koenigsberg to the shore of the Baltic Sea. Many died on the way from hunger and frost, those who lagged behind were shot. During these "death marches", at least 11 thousand prisoners of Stutthof died. The Nazis shot the survivors in the area of Palmniken (today the village of Yantarny in the Kaliningrad region of Russia).
On May 9, the Soviet soldiers-liberators in Stutthof were met by only a few hundred exhausted prisoners, according to some sources - about 200 people. They said that before retreating, the Germans had to blow up the crematorium and gas chamber, burn the barracks and destroy documents, which was partially done. From 1946 to 1947, three trials of the camp staff and management took place in Poland. Many of the defendants received death sentences.
Now there is a museum on the territory of Stutthof and excursions are held to preserve the memory of the darkest pages of history associated with the activities of German concentration camps.
In the Name of Life on Earth
Prisoners of Auschwitz in the first minutes after the liberation of the camp by the Red Army. © RIA Novosti / B. Fishman
The liberation of prisoners of Nazi concentration camps by Soviet troops was not just one of the stages of the Great Patriotic War, it was a kind of culmination of humanity and compassion shown by the soldiers of the Red Army in difficult wartime. Our soldiers have become a symbol of hope for all those who have already lost faith in salvation. Each liberated prisoner is a witness to this selfless feat, imbued with true humanism. We will always remember this and must do everything to ensure that nothing like this ever happens again.
The material was prepared with the support of the Research Institute of Military History of the Military Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation
We continue the struggle, we do not forget - "Understand fascism deeply, it will not die alone, crush it!"
D. KOUTSOUMBA'S VISIT TO THE NAZI HELL OF BUCHENWALD
During his visit there, Dimitris Koutsoumbas made the following statement translated from Greek:
"The moment will come when all... hearts will light up like a flame and burn to the root fascism, the rotten wound of the world... Long live Telmann and his brave comrades, who are mercilessly digging the grave of fascism" (M. Gorky).
In Buchenwald, the concentration camp where 56,000 people were exterminated, among them the leader of the Communist Party of Germany, Enst Telmann, the General Secretary of the Central Committee of the KKE, Dimitris Koutsoumbas, and the delegation of the Party visiting Germany, paid tribute to all those who founded with their lives the liberation from Nazi fascism.
The delegation was welcomed and guided by Holger Obbarius, head of educational programs at the monumental site.
Wreaths were laid at the site of the murder of Ernst Telmann, on the altar for the contribution of the Greek people to the struggle against fascism and at the monument to Fritz Kremer that surrounds the camp in an imposing magnificent composition that encloses mass graves of prisoners.
During his visit there, Dimitris Koutsoumbas made the following statement:
"We are in Buchenwald, in one of the many concentration camps of forced labor, martyrdom, in which millions of people were exterminated, among them many communists, militants, such as Ernst Telmann, General Secretary of the Communist Party of Germany, also Jews, anti-fascist fighters, Soviet soldiers and many of our Greek compatriots. We continue this struggle, we remember, we do not forget because we know that: 'Understand fascism deeply, it will not die alone, crush it'!"
The site with the three huge pits, where thousands of prisoners were buried, was chosen by the GDR state to erect a majestic monument leading "From Death and Struggle to Victory".
The visitor descends the Blood Ladder to the point where he meets the mass graves, from there begins the "Road of the Nations", with 18 large plaques on one side bearing the name of each country from which there were prisoners in Buchenwald, mainly those who paid the greatest blood tax.
At the end of the street stands the "Freedom Tower", deliberately visible from the city of Weimar, whose inhabitants claimed after the war that they "did not know" what was happening in the camp. The monument, therefore, aims to remind them of what happened and that anyone who does not react to pain and injustice, becomes, unwittingly, an accomplice. In front of the tower stands an impressive sculpture by Fritz Kremer, while a plaque has been placed inside the tower, which covers soil brought there from countries that experienced fascist atrocities.
In a space once synonymous with horror, today reigns the serenity of nature that richly surrounds it. The hell was founded in July 1937 and by 1945 it had become a place of imprisonment for 250,000 people from 32 countries with tens of thousands never seeing an exit. Today it stands as a monumental place, an unmistakable witness to the need not to be forgotten, not to cease for a moment the struggle against the womb that gives birth to fascism.
The visit of the General Secretary of the CC of the KKE, Dimitris Koutsoumbas, to Germany ends tomorrow, Sunday 11 May, with the last stop in Stuttgart where he will address a political gathering in the framework of the festival event of KNE (at the Clara Zetkin Haus). Alexandros Matsingos, a member of the Central Committee of KNE, will speak at the event and will be followed by a concert with the band "Common Mortals".
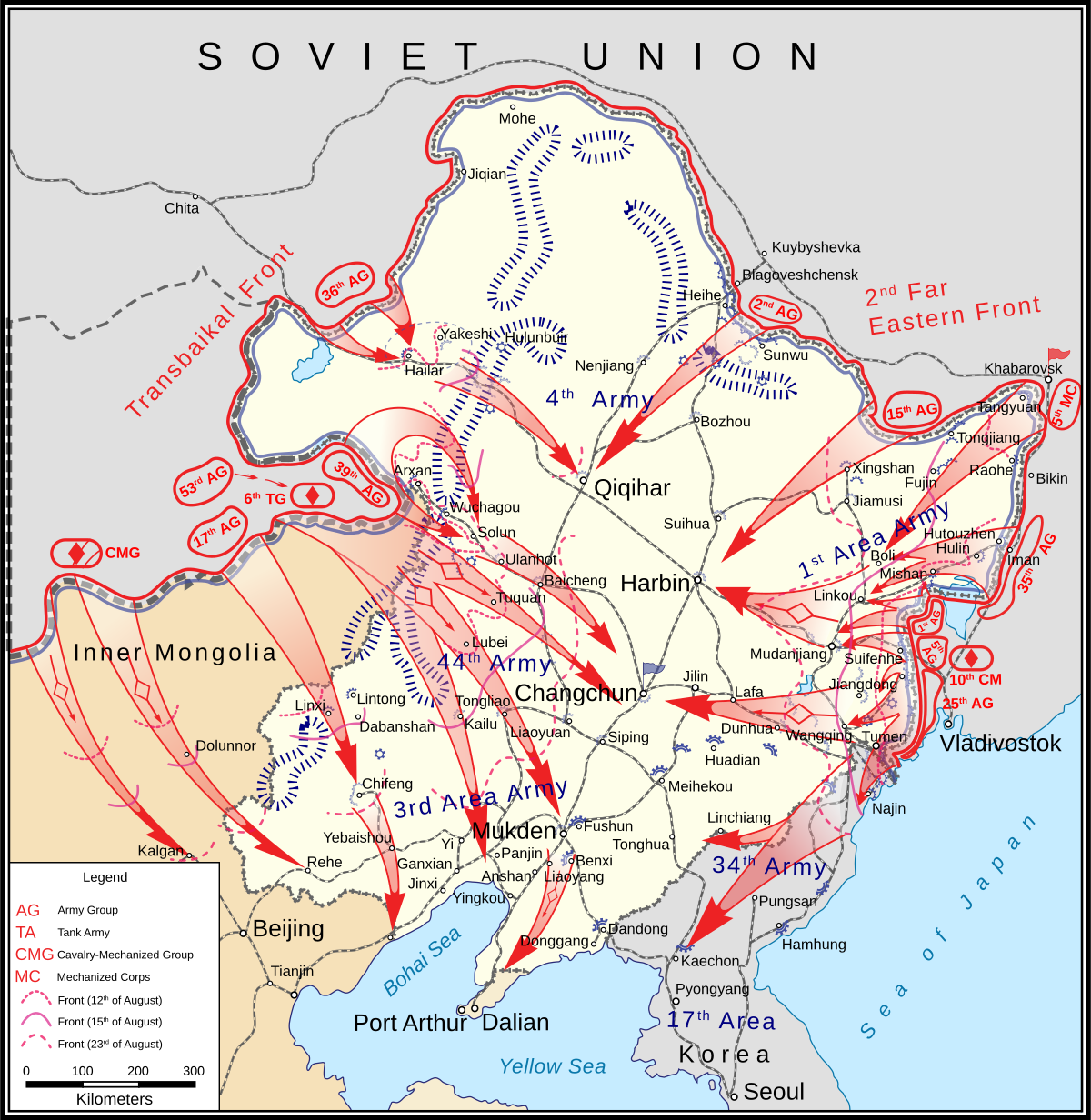
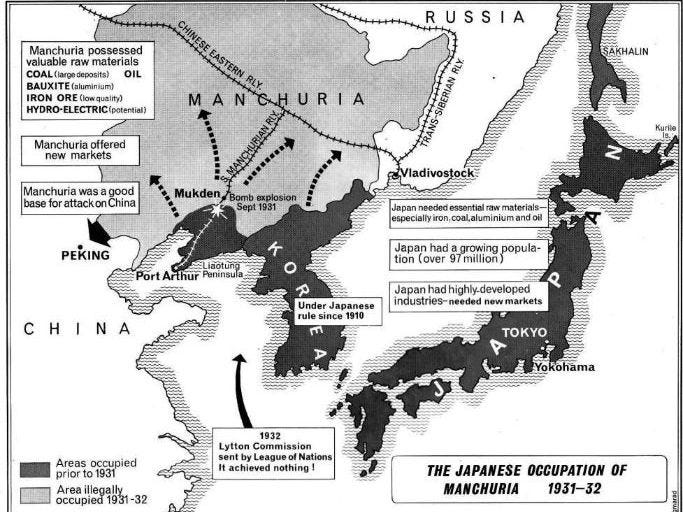
The Unknown War - The Last Battle of World War II Red Army Liberation of Manchuria
American Myth: It was not Truman’s A-Bombs that really ended the war in the Pacific, it was the Soviet Red Army’s defeat of the Japanese Army and threats to invade Japan that terrified the fascist Japanese elites.
The Final Death Blow to Japan in China:
General Zhukov’s Soviet Red Army invasion of Imperial Japanese occupied Manchuria
Soviet Red Army liberation of Harbin, China.
Country Estimated Total Civilian and Military Deaths
Soviet Union 24,000,000+
China 20,000,000+
Russia and China will never forget WWII victims – Putin
The two countries stand against neo-Nazism and militarism, the president has said
Moscow and Beijing remain staunch defenders of the historic truth and remember the countless people their countries lost during World War II, Russian President Vladimir Putin has said during talks with his Chinese counterpart Xi Jinping.
Xi is among the more than two dozen world leaders who are expected to attend the events in Moscow commemorating the 80th anniversary of the Soviet victory over Nazi Germany. The Chinese president is also poised to hold negotiations with Russian officials.
During a meeting on Thursday, Putin thanked his “dear friend” Xi for the visit and for joining him in celebrating a “sacred holiday for Russia.” “The sacrifices that both our nations made should never be forgotten. The Soviet Union gave 27 million lives, laid them on the altar of the Fatherland and on the altar of Victory. And 37 million lives were lost in China’s war for its freedom and independence. Under the leadership of the Communist Party, this victory was achieved,” he said.
Putin highlighted the significance of the triumph over fascism, adding that Russia and China “defend historical truth and the memory of the war and fight against current manifestations of neo-Nazism and militarism.”
The Russian leader also thanked Xi for inviting him to his country’s celebrations of its victory over Imperial Japan in WWII. “I will be glad to come back to friendly China on an official visit,” he said.
In echoing remarks, Xi emphasized shared historical memory and the strategic alignment between Beijing and Moscow. “The Chinese and Russian peoples, at the cost of heavy losses, achieved a great victory” and made an “indelible historic contribution to global peace and the progress of humanity,” he noted.
Russia and China have long enjoyed close ties, with the two countries describing their relations as a “no limits” partnership where there are “no forbidden zones.” Beijing has also consistently refused to support Western sanctions against Moscow over the Ukraine conflict.
Russia and China to Celebrate Victory Day Together Against Fascism
The Chinese leader’s three-day trip will include talks with Vladimir Putin and attendance at the Victory Day Parade
China's President Xi Jinping. © Wagner Meier/Getty Images
Stalin keeps his promise for deploying the Soviet Red Army against fascist imperial Japanese million-man Kwantung Army in China’s Manchuria
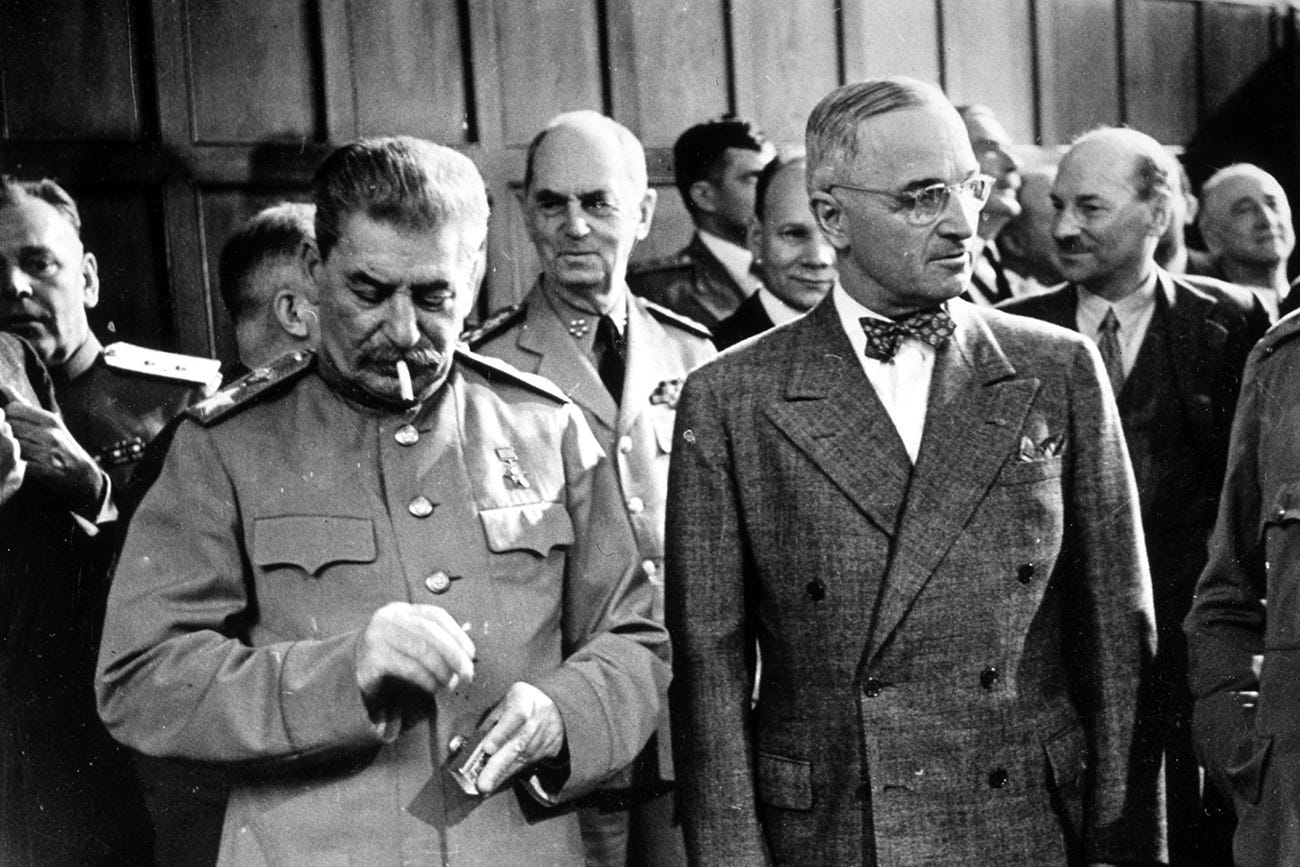
A picture of Soviet photographer Yevgeny Khaldei from July 1945 shows the participants of Potsdam Conference at the end of World War II. From left Josef W. Stalin (USSR), Harry S. Truman (USA) und Winston Churchill (Great Britain), who talk to the press.
July 1945 shows the participants of Potsdam Conference at the end of World War I1
Stalin keeps his promise to Truman and the Allies for deploying the Soviet Red Army against fascist imperial Japanese million-man Kwantung Army in China’s Manchuria which participated in the long ruthless occupation and genocide of Chinese peoples in Japan’s quest for its own Hitlerian-like “Asian Lebensraum” under Japan’s Imperial “Asian Co-Prosperity Sphere.” (Truman will later disavow the FDR/Stalin Yalta Agreements considering FDR not aggressive enough and “too soft on communism” a phrase that will become emblematic of the dawning of Truman/Churchill cold war era.)
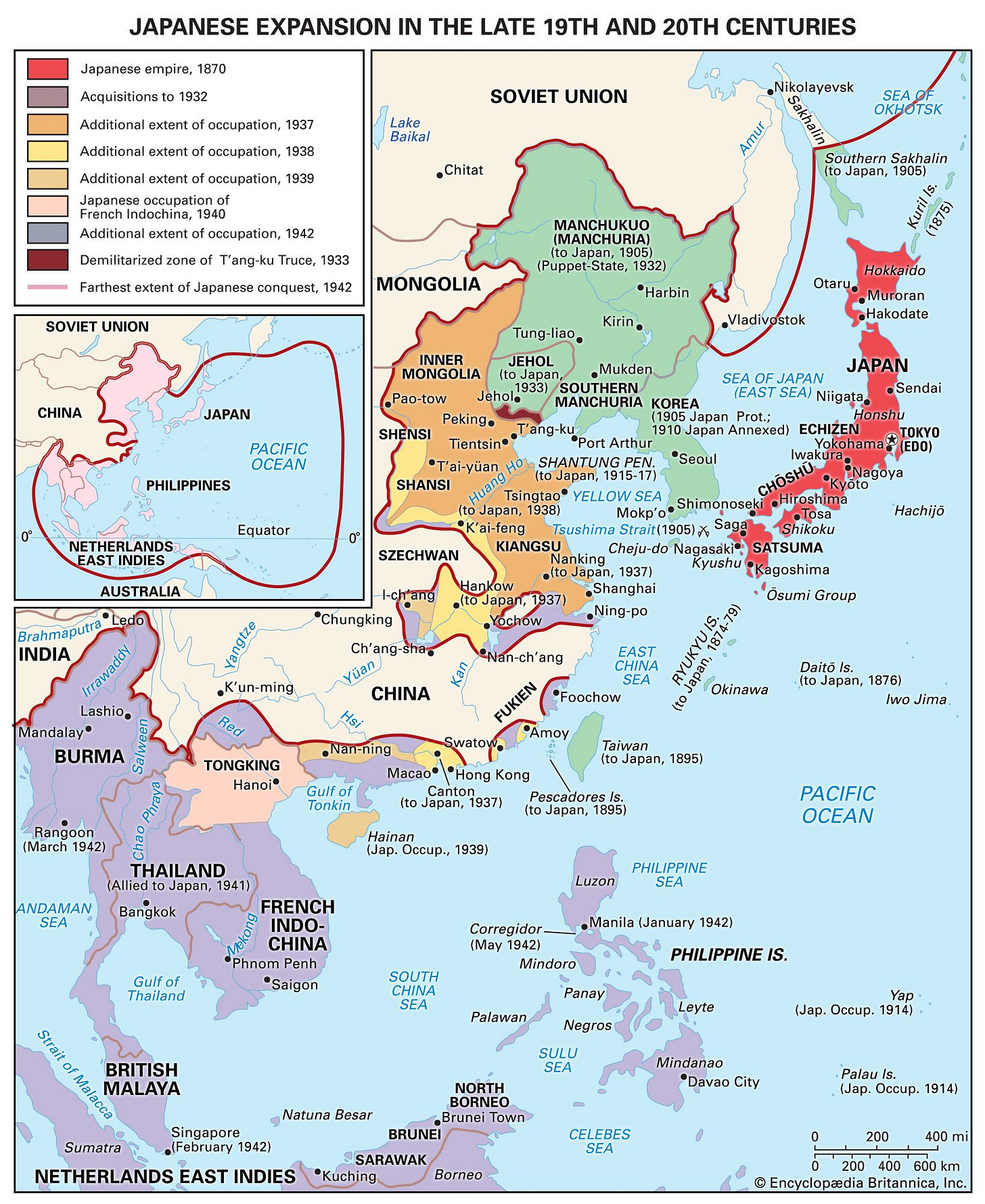
China Holocaust of 20,000,000+ dead during the Japanese Imperial occupation
Fascist imperial Japanese million-man Kwantung Army
The Unknown War - The Last Battle of World War II Red Army Liberation of Manchuria
American Myth: It was not Truman’s A-Bombs that really ended the war in the Pacific, it was the Soviet Red Army’s defeat of the Japanese Army and threats to invade Japan that terrified the fascist Japanese elites.
The Final Death Blow to Japan in China:
General Zhukov’s Soviet Red Army invasion of Imperial Japanese occupied Manchuria
Soviet Red Army liberation of Harbin, China.
Russia and China to Celebrate Victory Day Together Against Fascism
The Chinese leader’s three-day trip will include talks with Vladimir Putin and attendance at the Victory Day Parade
China's President Xi Jinping. © Wagner Meier/Getty Images
Country Estimated Total Civilian and Military Deaths
Country Estimated Total Civilian and Military Deaths
China 20,000,000+
Russia and
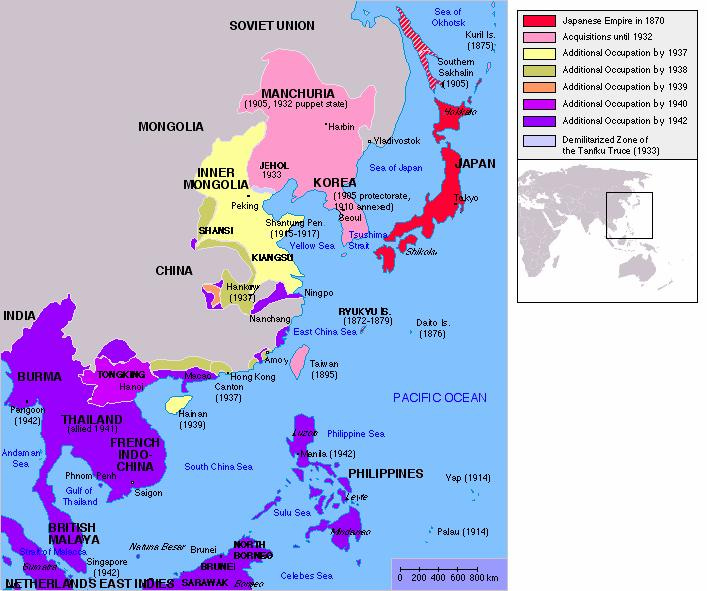
Like Euro-Nazi Hitler Mass Death-Camps scattered throughout Eastern Europe and Poland, the Japanese fascist regime had their own including, like Nazi doctor Mengle’s grizzly medical experiment projects.
So, too, did the Japanese have their own “Mengle” General Ishii who was in charge of the bacteriological laboratory, Unit 731, in Harbin produced horrific human experiments on thousands of Chinese, later, US secret services recruited many of those who worked on both biowarfare projects into the US biowarfare institutions.
Blowback: America's Recruitment of Nazis and Its Destructive Impact on Our Domestic and Foreign Policy
(A side note that no one likes to talk about is the fact that after the tremendous losses of US forces in brutal Island-hopping campaigns in the Pacific and the eventual potential losses of all out invasion of mainland Japan, US forces, especially US marines, were not too happy about yet another “hit the beach operation.”
Like their US G.I. bretheren on the western front, some thought the Red Army’s invasion of Manchuria to break the back of Japanese Imperial Army was a good idea. “So the rest of us could go home in one piece.” So, Truman’s advisors considered yet another Red Army bloodletting would help to save American lives.)
US and western cold war historians until recently either censored or downplayed USSR’s role in the final defeat of the World War II in order to rebrand the Japanese fascists as now America’s “good anti-commie guys” like their axis Euro-nazi/fascist allies. In fact, the US went so far as to protect some of the most vicious and cruel Japanese war criminals from prosecution during the Tokyo Wars Trials. One reason why today’s China still seeks official US - Japanese disclosures and apologies for protecting mass murderers.
Holocaust in the East: Map of the Japanese Empire in Asia/Pacific Basin
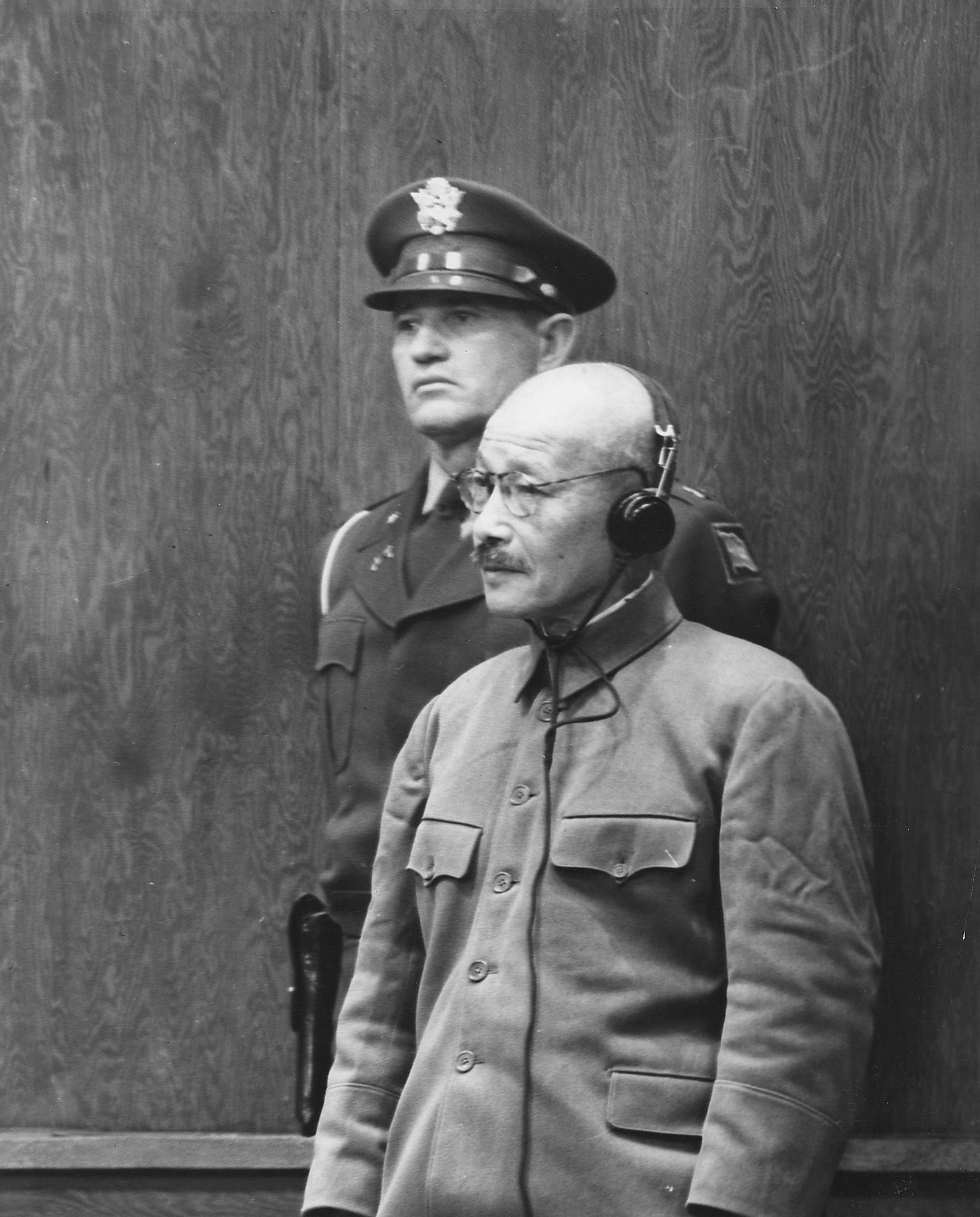
In Tokyo, Japan, Hideki Tojo, former Japanese premier. Caught some big fish but let slip the rest in the name of fighting Chinese communism in Asia.
Much is the same for post-war Euro-Nazi and Euro-Fascist elites who eventually integrated back into the US cold war against the USSR under their NATO banner.
US/UK/NATO’s Nazi/Fascist Ratlines saved and recruited thousands of nazis and fascists elites and war criminals into the western anti-communist cold war.
Real History is more interesting than current conventional histories and historians which hide more than reveal the truth of the past. U.S. national security state’s secret recruitment and coverup of German and Japanese war criminals after World War II has been documented internationally yet US elites refuse to acknowledge this until recent new histories have been declassified made public.
Kremlin aide reveals which world leaders to attend Victory Day parade
Foreign dignitaries are arriving in Moscow ahead of the May 9 celebrations, Yury Ushakov has said
© Maxim Shipenkov/Pool Photo via AP
Foreign leaders and envoys from 29 countries will attend Russia’s Victory Day parade later this week in Moscow, presidential aide Yury Ushakov has announced. The May 9 event commemorates 80 years since the Soviet Union’s triumph over Nazi Germany in the Second World War.
The international guests are also expected to meet with Russian President Vladimir Putin, Ushakov added. This year’s landmark celebrations will include a traditional military parade on Red Square.
Chinese President Xi Jinping, Brazilian President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva, Serbia’s President Aleksandar Vucic, Venezuela’s President Nicolas Maduro, Egypt’s President Abdel Fattah El Sisi, and Slovakia’s Prime Minister Robert Fico will be among the leaders present, Ushakov confirmed to journalists on Tuesday.
Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi will not be among the visitors due to mounting tensions with Pakistan. However, New Delhi will still be represented by a high-level delegation.
Vucic is expected to attend the celebrations despite a recent health scare, Serbian Deputy Prime Minister Sinisa Mali said on Monday.
Officials in Brussels previously warned Vucic that his presence in Moscow would be held against Belgrade’s EU aspirations.
Fico has also confirmed his attendance.
The celebration “is truly becoming a major international event serving as an indicator of Russia’s growing authority in the world,” Ushakov stated.
Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orban declined an invitation to attend.
The US ambassador to Russia, Lynne Tracy, was also invited. However, according to Ushakov, she has not confirmed whether she will attend.
The Victory Day parade will feature military units from 13 countries, including China, Egypt, and Vietnam, among others, the aide said.
Military veterans from several countries, including Armenia, Israel, Mongolia, and the US, are also expected to attend the parade.
Last week, Ukraine’s Vladimir Zelensky urged foreign leaders to avoid visiting Moscow, citing potential security risks. Russian officials accused Zelensky of endangering the safety of civilians attending the May 9 events. Fico dismissed the threats as “ridiculous.”
Kremlin reveals details of Xi’s visit to Russia
The Chinese leader’s three-day trip will include talks with Vladimir Putin and attendance at the Victory Day Parade
China's President Xi Jinping. © Wagner Meier/Getty Images
Chinese President Xi Jinping will visit Russia from May 7 to 10 to attend the Victory Day Parade in Moscow and hold talks with Russian President Vladimir Putin, the Kremlin announced on Sunday. The visit marks the 80th anniversary of the Soviet Union’s victory over Nazi Germany.
Russia will hold its annual Victory Day parade on Red Square on May 9. More than 20 foreign leaders are expected to attend the commemoration in the Russian capital, including Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko, Slovak Prime Minister Robert Fico, Serbian President Aleksandar Vucic, Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan, among others.
In April, Russian President Vladimir Putin first announced that he would meet with the Chinese leader during the World War II victory celebrations in Moscow. Putin later proposed a 72-hour unilateral ceasefire in Ukraine to coincide with the festivities. Ukraine’s Vladimir Zelensky turned down the proposal, calling it a “theatrical performance” and instead pushed for a broader 30-day unconditional truce. Moscow officials said such a pause would let Kiev regroup and resupply.
Following this, Zelensky warned global leaders heading to Moscow that Ukraine cannot assure their safety.
“During the negotiations, key issues regarding the further development of comprehensive partnership and strategic interaction will be discussed, as well as current problems on the international and regional agenda,” the statement from the Kremlin said. “The signing of a number of bilateral intergovernmental and interagency documents is planned.”
The visit will be Xi’s third to Russia since the escalation of the Ukraine conflict in 2022. China has maintained a position of neutrality in the conflict but has refused to blame Russia for the hostilities and has condemned the Western sanctions on Moscow, accusing the US of having a “Cold War mentality” based on confrontation.
Related compilation of histories and sources:
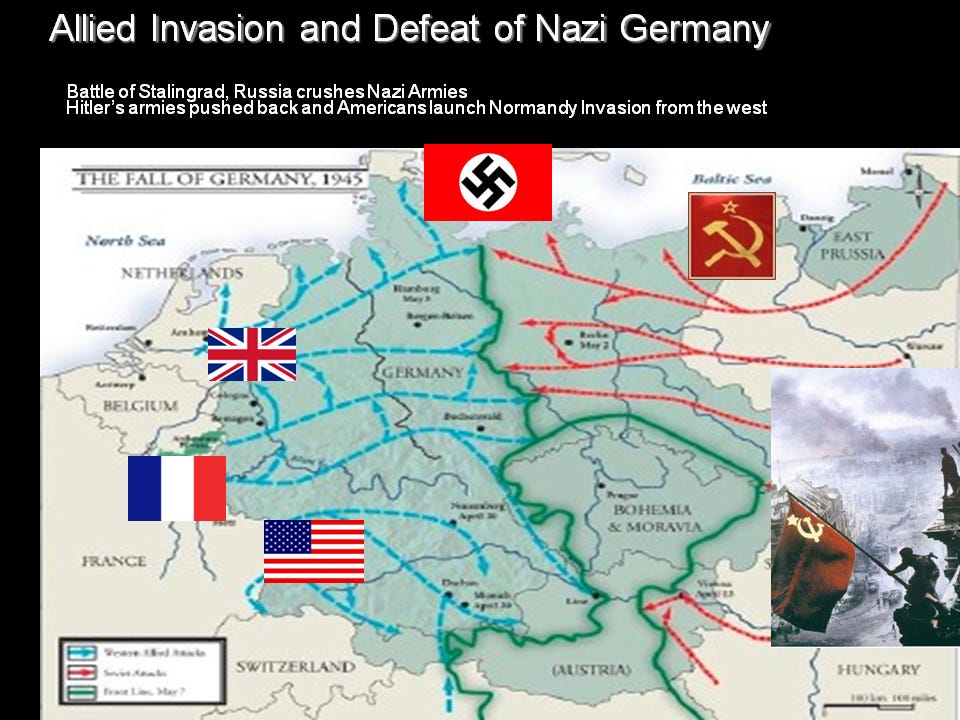
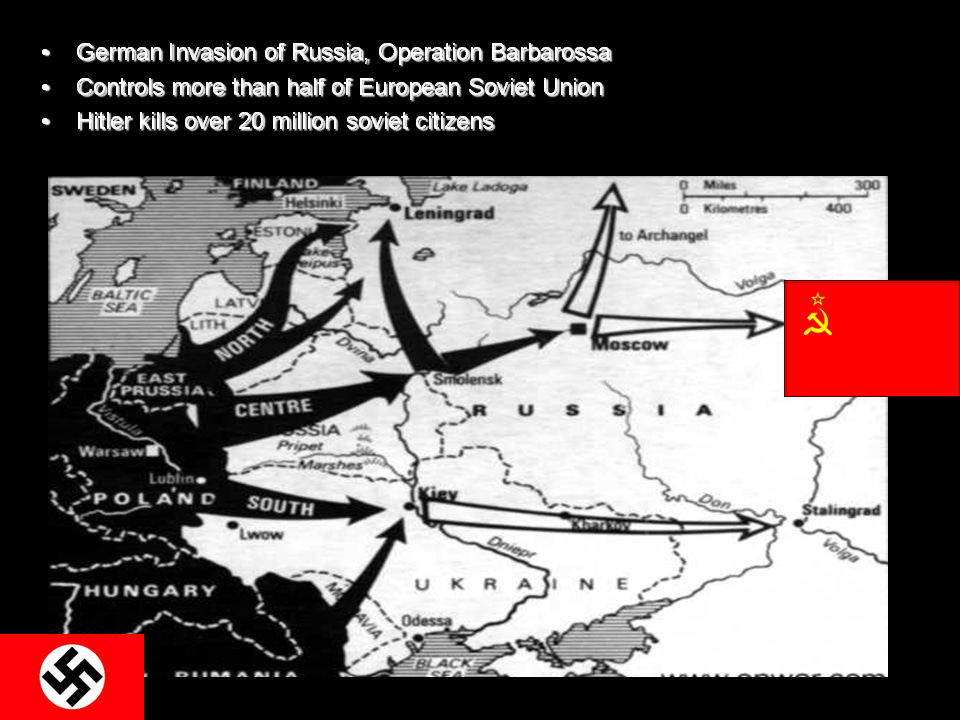
The Battle of Berlin and the Red Army defeat of the Nazi Regime.
World War II Through Russian Eyes
US/UK Allies enter late:
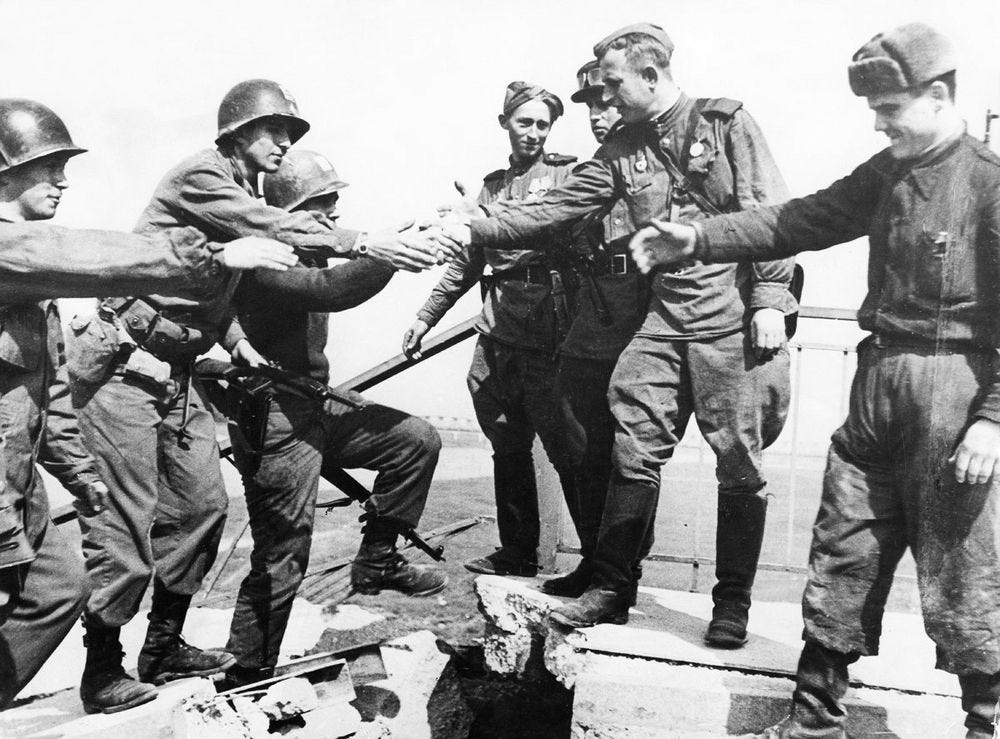
Second Front invasion at Normandy after massive Red Army losses and victories in the East.
US G.I.’s and USSR Red Army Soldiers meetup at the Elbe River, Nazi Germany conquered.
Related histories/sources
Historical Background to May 9th Russia Victory Day
Did World War II Really Ever End?
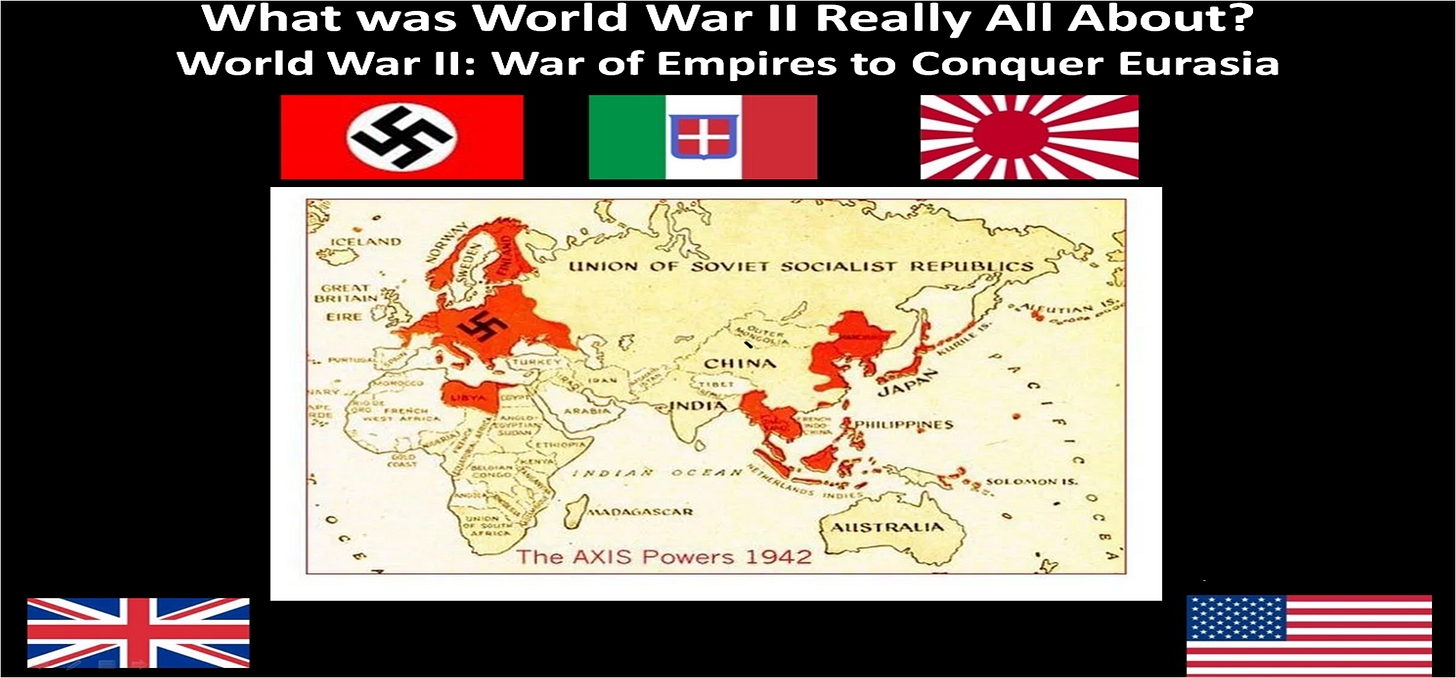
Conventional WWII Histories have an Anglo-American Western-centric bias tending to downplay the reality that World War II was principally a war of western empires vying for the ultimate prize: The Conquest of Eurasia between Western Powers US, UK, Europe vs. Nazi Germany, Italy and Japanese fascist empires.
WESTERN COLD WAR HISTORIANS RE-WRITING HISTORY:
Cold War Ideological Bias of Western-Centric Histories of World War II
Creating a false Nazi / Soviet historical comparisons
Richard Overy, historian & author Soviet Communism v German Nazism discusses the conventional western cold war histories of World War II and why they are creating a false Nazi / Soviet historical comparison which formed the basis for western cold war histographies of World War II.
World War II Really Never Ended. Why?
Western memory of WWII is basically fan fiction
Trump needs a serious History Lesson - US did most to win both world wars – Trump
Past is Prologue: April is the Cruelest Month for Nazis and Imperialists: A History of Two Wars
Who Helped and Supported Hitler’s Anti-Soviet War?
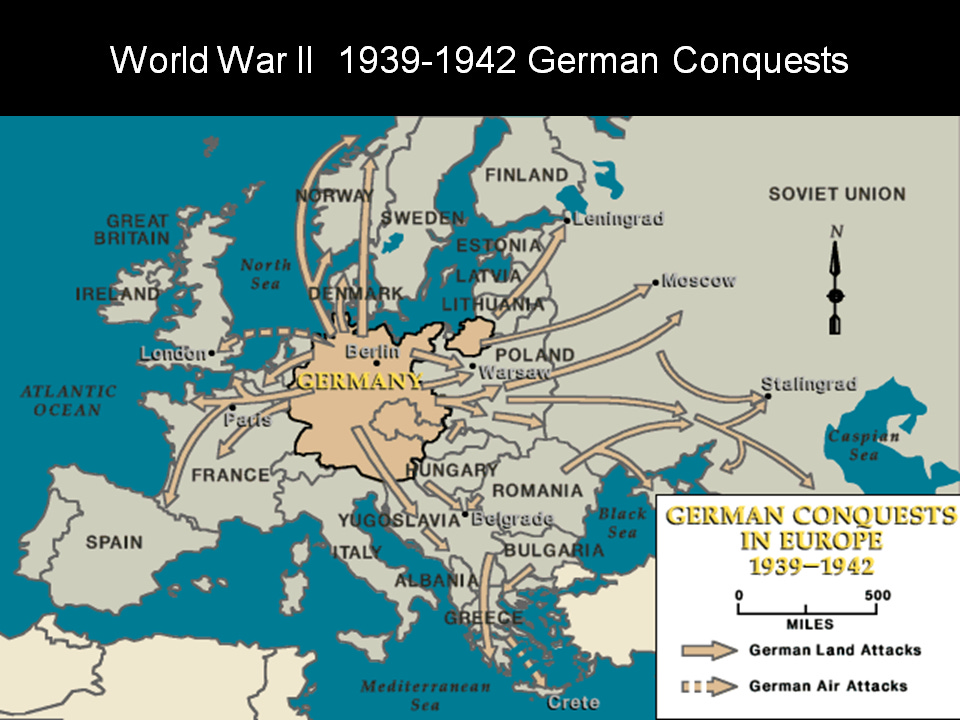
Euro-Nazi Empire occupies Europe, later supported by Collaborationist European axis regimes in order to support the Nazi German war of annihilation against USSR.
Many Euro-Nazi/Fascist regimes include many of today’s western European nations: Norway, Finland, Baltic states, Hungry, Romania, Austria, France, Belgium, Netherlands, Denmark and other regimes that sympathized with the Axis forces and provided troops and supplies from their respective countries in order to sustain Europe’s invasion and eventual annihilation of the Soviet Union.
US/UK Allies enter late Second Front invasion at Normandy after massive Red Army losses and victories in the East.
Truman’s Yalta Betrayal of USSR Ally
Truman’s Yalta Betrayal of USSR
Truman’s Yalta Betrayal of USSR begins after death of FDR who negotiated with Stalin the post-war world order with the understanding that the US and USSR would take the lead through collaborative efforts in reconstructing a war-torn Europe and creating a United Nations system to replace the failed League of Nations.
Yet, western anti-communist elites including Truman and Churchill colluded to systematically disavow Yalta which would lead a confrontation with the USSR by enunciating and implementing Churchill’s “Iron Curtain Speech” which was to set the tone of future ideological cold warfare doctrines and resurrected Euro-Nazism/Fascism under the guise of US national security state alliances from NATO in Europe and throughout the rest of the post-war world.
Truman’s Yalta Betrayal of the US/USSR Alliance and Agreement leads to Cold War era
Roosevelt and Truman on Yalta: The Origins of the Cold War on JSTOR
Truman/Churchill Cold War Anti-Communist Doctrine and the Yalta Betrayal of USSR
U.S. Containment Policies were not only meant to "contain" the alleged Soviet threat of "world domination", which in reality was based on an exaggerated 'threat' conjured up by U.S. 'red scare' propaganda campaigns such as 'McCarthyism', but to contain the threat of national independence movements that threatened market access to U.S. multinational corporate interests in the Global South.
US elites’ cold war fanatical anti-communism betrays the victorious WWII US/USSR anti-fascist alliance.
When Nazis and Fascists Become America’s “Anti-Commie Good Guys.”
Truman/Churchill Cold War Anti-Communist Doctrine and US national security state elites embrace defeated Nazis and Fascists in cooperative cold war anti-communist crusades.
Related compilation of histories and sources:
Past is Prologue: April is the Cruelest Month for Nazis and Imperialists: A History of Two Wars
World War II Really Never Ended. Why?
Trump needs a serious History Lesson
Western memory of WWII is basically fan fiction